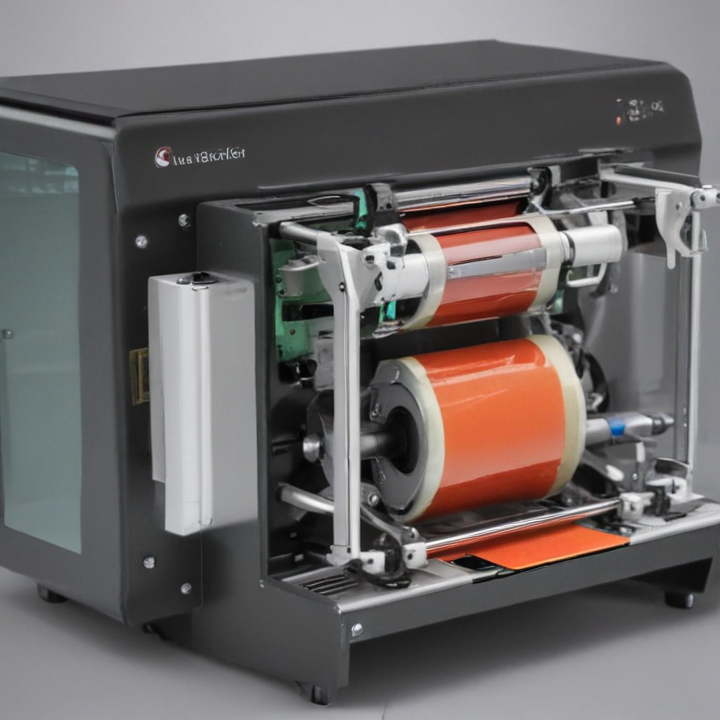
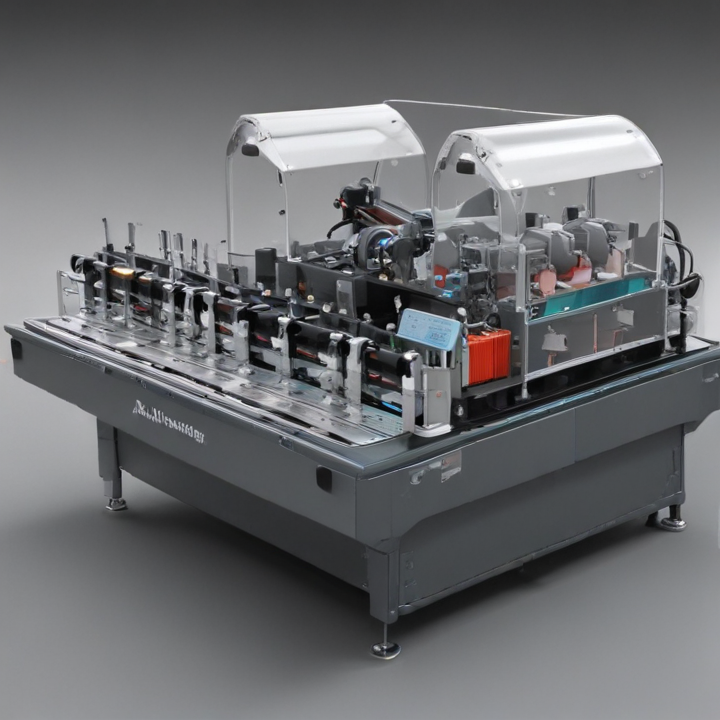
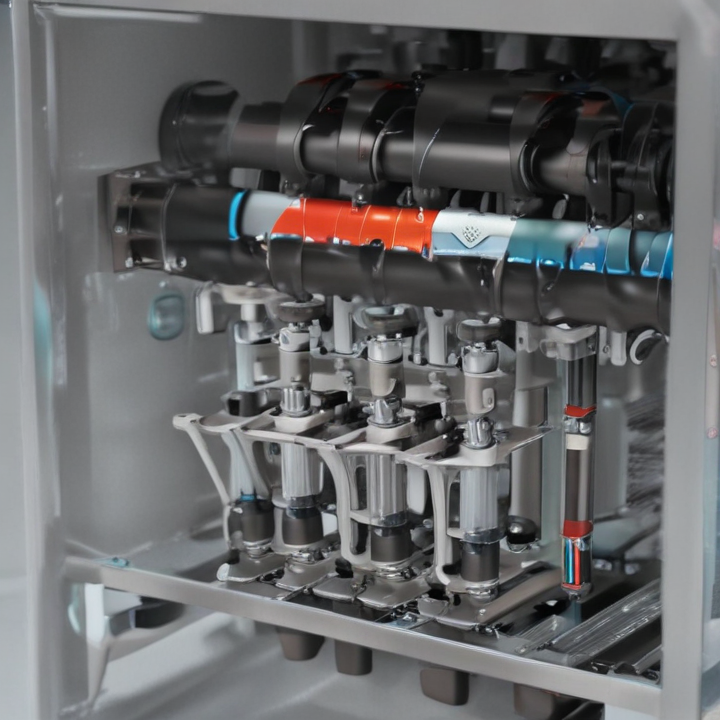
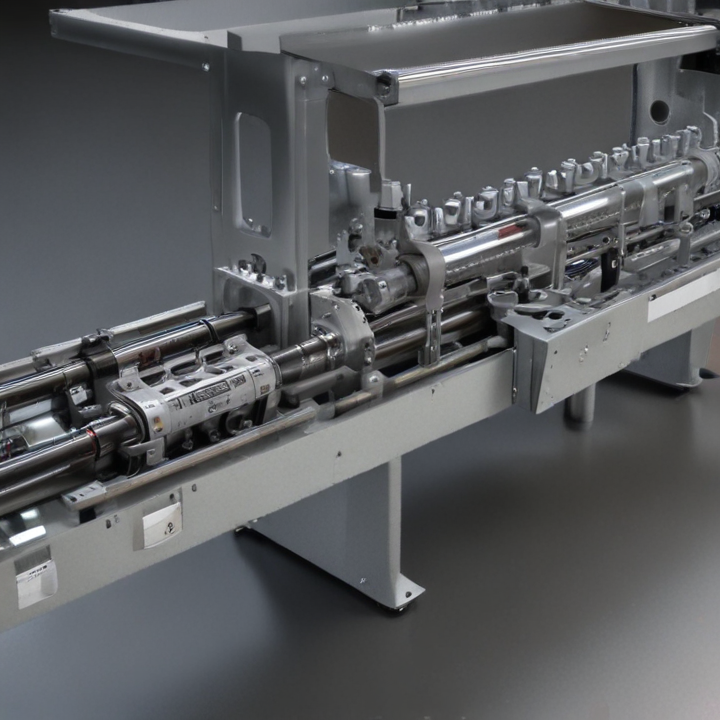
List Technical Parameters of “automatic tube labeler”
An automatic tube labeler is a sophisticated piece of laboratory equipment designed for the precise and efficient labeling of specimen tubes in medical, clinical, and research settings. Here are the key technical parameters typically associated with an automatic tube labeler:
1. Labeling Speed: The rate at which the machine can label tubes, usually measured in tubes per minute (tpm).
2. Tube Diameter Range: The range of diameters the machine can handle, ensuring compatibility with different tube sizes.
3. Tube Length Range: The length specifications of tubes that the labeler can accommodate.
4. Label Size: The dimensions of the labels that can be applied, including both height and width.
5. Label Roll Capacity: Maximum outer diameter and width of the label roll that the machine can hold.
6. Print Resolution: For systems with an integrated printer, the resolution at which data can be printed on the labels, measured in dots per inch (DPI).
7. Print Speed: For integrated printers, the speed at which labels can be printed, often measured in millimeters per second (mm/sec).
8. Material Compatibility: Types of label materials the machine can handle, such as paper, polyester, and vinyl.
9. Software Integration: Compatibility with laboratory information systems (LIS) and other software for data input and management.
10. Power Requirements: Voltage and current specifications needed to operate the machine.
11. Operational Modes: Various modes like continuous, batch, or single labeling options to match different workflow needs.
12. User Interface: Type of interface, such as touchscreen, buttons, or a connected computer, for machine control and configuration.
13. Dimensions: Physical dimensions of the machine (length, width, height) to ensure proper fit in the laboratory space.
14. Weight: The weight of the machine, which is crucial for portability and installation considerations.
15. Environmental Conditions: Optimal operating temperature, humidity range, and storage conditions to maintain machine performance.
16. Safety Features: Inbuilt safety measures like emergency stop buttons, enclosure guards, and warnings.
These parameters collectively define the functionality, efficiency, and usability of an automatic tube labeler, making it an indispensable tool in laboratory automation.
List Product features of “automatic tube labeler”
An “automatic tube labeler” is a specialized piece of equipment designed to efficiently apply labels to tubes, typically used in laboratories, medical facilities, or manufacturing environments. Here are the key features of an automatic tube labeler:
1. Automated Operation: The device automatically feeds, positions, and applies labels, minimizing manual labor and human error.
2. High Throughput: Capable of labeling hundreds to thousands of tubes per hour, significantly increasing productivity.
3. Precision Labeling: Utilizes advanced sensors and positioning mechanisms to ensure labels are applied accurately and consistently on the target area of the tube.
4. Flexible Label Sizes: Accommodates various label sizes and shapes, making it versatile for different tube specifications.
5. Tube Size Compatibility: Supports a wide range of tube diameters and lengths, from small vials to larger sample containers.
6. User-Friendly Interface: Equipped with a touch screen or control panel for easy setup, operation, and monitoring of the labeling process.
7. Barcode and QR Code Integration: Capable of printing and reading barcodes and QR codes for efficient tracking and identification of samples.
8. Data Management: Integrated software for logging and managing label information, often with connectivity to Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS).
9. Adjustable Settings: Customizable settings for label placement, speed, and adhesion pressure to match specific requirements.
10. Robust Construction: Built with durable materials to withstand continuous operation in demanding environments.
11. Safety Features: Includes emergency stop buttons and protective guards to ensure user safety during operation.
12. Easy Maintenance: Designed for quick and easy maintenance, with accessible components and straightforward cleaning procedures.
13. Multi-Tube Handling: Some models offer the ability to label multiple tubes simultaneously, further enhancing efficiency.
14. Portability: Compact and lightweight designs are available for easy relocation and integration into various workflows.
15. Environmental Adaptability: Operates reliably in different environmental conditions, maintaining performance in labs, factories, or field settings.
These features collectively make the automatic tube labeler an essential tool for enhancing accuracy, efficiency, and traceability in various applications.
List Application of “automatic tube labeler”
An automatic tube labeler is a specialized piece of equipment designed to apply labels to cylindrical objects like test tubes, vials, and other types of tubes. Here are its primary applications:
1. Healthcare and Laboratories:
– Specimen Identification: Ensures accurate labeling of blood, urine, tissue, and other samples to prevent mix-ups.
– Pharmaceuticals: Facilitates precise labeling of drug samples, reagents, and compound libraries.
2. Biotechnology:
– Research Labs: Automates labeling of DNA, RNA, and protein tubes used in experiments.
– Cryogenic Storage: Suitable for labeling tubes that will be stored in extremely low temperatures.
3. Clinical Diagnostics:
– Pathology Labs: Helps in the identification and organization of biopsy samples.
– Genetic Testing: Streamlines the labeling of samples for sequencing and genetic analysis.
4. Food and Beverage Industry:
– Quality Control: Labels samples for microbial and chemical testing.
5. Chemical Industry:
– Sample Management: Ensures accurate labeling of chemical reagents and samples for testing and research.
6. Environmental Science:
– Sample Collection: Facilitates labeling of water, soil, and air samples for contamination testing.
7. Agrochemicals:
– Seed and Soil Testing: Labels samples for research on crop improvement and soil health.
8. Industrial Manufacturing:
– Component Tracking: Labels parts and components for traceability in production processes.
9. Education and Training:
– Laboratory Training: Used in academic labs for teaching proper sample management.
By automating the labeling process, these machines enhance efficiency, reduce human error, improve traceability, and ensure compliance with industry standards. This is especially crucial in environments where accurate sample identification can have significant consequences, such as healthcare and scientific research.
List Various Types of “automatic tube labeler”
Automatic tube labelers are specialized machines designed to apply labels to tubes efficiently and accurately. They come in various types tailored to different industry requirements and tube specifications. Here’s a list of common types:
1. Wrap-Around Tube Labelers: These machines apply labels that wrap around the entire circumference of the tube. Ideal for cylindrical tubes in pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and laboratory testing.
2. Horizontal Tube Labelers: Specifically designed for tubes that are labeled while lying horizontally. Often used for blood collection tubes and other similar small-diameter tubes.
3. Vertical Tube Labelers: These labelers apply labels to tubes standing vertically. Often utilized for larger tubes or containers in industrial and food packaging.
4. Semi-Automatic Tube Labelers: This type offers partial automation, where an operator feeds the tubes into the machine, and the machine completes the labeling process. Suitable for smaller-scale operations.
5. Fully Automatic Tube Labelers: Designed for high-speed operations, these machines handle tube feeding, labeling, and sometimes sorting or packing without human intervention. They are ideal for large-scale manufacturing.
6. Heat-Shrink Tube Labelers: These utilize heat to shrink label sleeves around the tube, providing a tight and durable labeling solution. Commonly used for electronics and wiring.
7. Laser Tube Labelers: These labelers use laser technology to engrave or etch information directly onto the tube’s surface. Ideal for applications requiring permanent marking, such as medical tubing.
8. Print and Apply Tube Labelers: These systems print labels in real-time and immediately apply them to tubes. Useful for applications requiring variable data or barcodes.
9. Rotary Tube Labelers: Employ a rotary system to position tubes for labeling, ensuring precise label placement. Often used in industries requiring high precision.
10. Pressure-Sensitive Tube Labelers: Use pressure-sensitive adhesives to apply labels, offering flexibility in label material and design. Suitable for a variety of tube materials.
Each type of automatic tube labeler offers specific benefits and is selected based on the particular needs of the application, such as volume, tube size, and industry standards.
Custom Manufacturing Options for automatic tube labeler
When seeking custom manufacturing options for an automatic tube labeler, several key features and considerations can optimize functionality for your specific needs.
1. Label Size and Shape Versatility: Ensure the machine can handle various label dimensions and shapes. Customizable software can allow for easy integration of different templates.
2. Speed and Throughput: Custom machines can be tailored to match your production speed requirements. High-speed models with variable adjustments help maintain efficiency without compromising quality.
3. Material Compatibility: Specify the range of tube materials and diameters the labeler must handle, such as plastic, glass, or metal. Adjustable fixtures and sensors enhance compatibility and reduce changeover times.
4. Printing Capabilities: Integrate advanced printing technologies like thermal transfer or inkjet printers, which can add barcodes, batch numbers, and expiry dates directly during the labeling process.
5. Automation Level: Choose between semi-automatic and fully automatic models. Fully automated machines with robotic arms or conveyor integrations reduce manual handling and improve precision.
6. User Interface: A customizable, user-friendly interface simplifies operation and training. Look for touchscreen controls and intuitive software that facilitate easy adjustments and diagnostics.
7. Quality Control Features: Incorporate vision systems or sensors to ensure correct label placement and detect defects, which helps maintain high-quality output.
8. Space and Footprint Considerations: Design the machine to fit within your existing production space. Compact models can save valuable workspace and are often more energy-efficient.
9. Connectivity: Ensure the machine supports Industry 4.0 standards for easy integration with existing manufacturing execution systems (MES) and other digital infrastructure.
10. Durability and Maintenance: Opt for robust materials and components to prolong service life. Features like quick-release parts and modular designs can facilitate easier maintenance and repairs.
Partnering with a specialized manufacturer who offers bespoke design services will ensure the automatic tube labeler meets all your operational needs efficiently while maintaining high performance and reliability.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “automatic tube labeler”
### Quality Control and Manufacturing Process of an Automatic Tube Labeler
Manufacturing Process:
1. Design and Engineering:
– Develop detailed blueprints and CAD models.
– Simulate performance and efficiency using software.
2. Material Procurement:
– Source high-quality components like motors, sensors, and labeling mechanisms.
– Use ISO-certified suppliers for consistent quality.
3. Fabrication:
– Use CNC machines and 3D printers for precision parts.
– Conduct welding, cutting, and assembly in-house.
4. Component Assembly:
– Assemble individual components such as the conveyor system, labeling head, and control panel.
– Follow a modular approach for easy troubleshooting and maintenance.
5. Electrical Integration:
– Install sensors, wiring, and control systems.
– Program PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers) for operation.
6. Initial Testing:
– Conduct dry runs to check for mechanical issues.
– Implement software debugging for efficient operation.
7. Final Assembly:
– Integrate all subsystems into the main frame.
– Apply finishing touches and branding.
Quality Control:
1. Incoming Material Inspection:
– Verify dimensions, material properties, and conformities using micrometers and calipers.
– Conduct vendor audits periodically.
2. In-Process Quality Control:
– Monitor assembly stages using checklists.
– Perform sub-assembly testing for functional validation.
3. Functional Testing:
– Conduct system checks to ensure labeling accuracy, speed, and reliability.
– Use test cases to simulate real-world operational conditions.
4. Final Inspection:
– Carry out thorough visual and performance testing.
– Validate parameters like label alignment, adhesion, and throughput.
5. Quality Documentation:
– Maintain detailed records for traceability.
– Implement corrective actions for any deviations.
6. Customer Feedback Loop:
– Gather performance data post-deployment.
– Implement design improvements based on feedback.
By robustly integrating quality control within the manufacturing process, the reliability and efficiency of automatic tube labelers can be consistently ensured.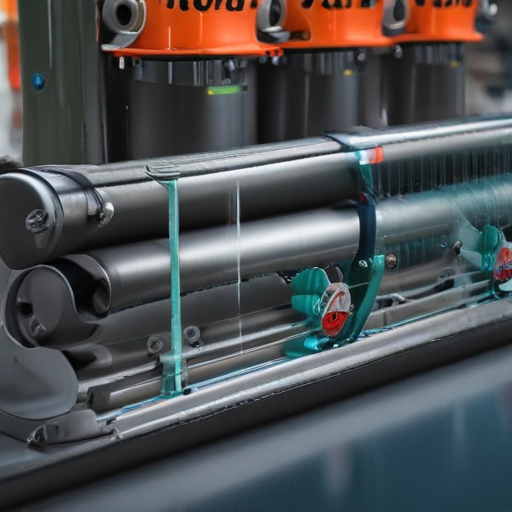
How to use “automatic tube labeler”
Using an automatic tube labeler is a straightforward process, but it requires careful attention to detail to ensure proper operation. Follow these general steps:
1. Setup the Machine:
– Unbox and Position: Place the labeler on a stable surface.
– Power Connection: Plug it into an appropriate power source.
– Load Labels: Insert the roll of labels into the designated holder, ensuring they are properly aligned with the feed path.
– Adjust Settings: Configure settings like label size, spacing, and speed using the control panel.
2. Prepare Tubes:
– Clean Tubes: Ensure tubes are free of dust and moisture for better label adhesion.
– Load Tubes: Place the tubes into the feeding mechanism. Depending on the machine design, tubes may need to be loaded manually or via an automated feeder.
3. Calibration:
– Test Run: Run a few test labels to ensure proper alignment and adhesion.
– Adjust as Needed: Fine-tune settings on the control panel if labels are misaligned or not sticking properly.
4. Labeling Process:
– Initiate Labeling: Press the start button to commence labeling. The machine will automatically apply labels to each tube.
– Monitor Operation: Keep an eye on the process to ensure continuous operation and address any issues, like label jams, immediately.
5. Post-Labeling:
– Unload Tubes: Carefully remove labeled tubes, inspecting for correct placement and adhesion.
– Turn Off Machine: Power down the labeler when done and perform any necessary cleaning or maintenance as per the user manual.
6. Maintenance:
– Clean Regularly: Wipe down the machine to remove any adhesive residue.
– Check Components: Inspect rollers, sensors, and other parts regularly to ensure longevity and optimal performance.
By following these steps, you can efficiently use an automatic tube labeler to streamline your labeling process. Always refer to the specific user manual for detailed instructions and safety guidelines.
List Properties and Terms of “automatic tube labeler”
An automatic tube labeler is a specialized machine used primarily in laboratory and industrial settings for the precise and efficient labeling of tubes, such as test tubes, blood collection tubes, and sample vials. Below, the key properties and terms associated with an automatic tube labeler are summarized:
### Properties:
1. Accuracy: Ensures correct label placement with high precision to prevent misidentification.
2. Speed: Capable of labeling a high volume of tubes rapidly, enhancing productivity.
3. Consistency: Delivers uniform labeling, reducing human error and ensuring standardization.
4. Versatility: Can accommodate various tube sizes and shapes.
5. Automation: Minimizes manual intervention, thereby reducing labor costs and human effort.
6. Calibration: Equipped with features to calibrate for different tube types and label sizes.
7. Integration: Often integrates with laboratory information management systems (LIMS) for streamlined data handling.
8. Durability: Built to withstand continuous operation and harsh laboratory conditions.
### Terms:
1. Label Format: Refers to the size, shape, and type of label the machine can handle (e.g., adhesive, thermal transfer).
2. Throughput: The number of tubes labeled per unit of time, typically measured in tubes per minute.
3. Barcode Output: Includes options for 1D and 2D barcodes to support tracking and data management.
4. Feeding Mechanism: The method by which tubes are supplied to the labeling station, which could be manual or automatic.
5. Label Sensors: Detect the presence and position of labels to ensure correct application.
6. Error Detection: Systems in place to identify and flag incorrect or incomplete labeling.
7. Print Resolution: The quality of text and barcode prints, usually measured in dots per inch (DPI).
8. Maintenance: Routine checks and maintenance provisions to ensure long-term reliability.
9. User Interface: The control panel or software interface used by operators to input labeling parameters and control machine functions.
10. Compliance: Adherence to industry standards and regulations, such as CE marking for safety and quality assurance.
These properties and terms govern the functionality and application of automatic tube labelers, making them indispensable in settings where precision and efficiency are crucial.
List The Evolution history of “automatic tube labeler”
The evolution of the automatic tube labeler intertwines with advancements in automation, computing, and material science.
Early 20th Century: Manual Labeling
Labor-intensive manual labeling predominates, reliant on human effort and prone to inconsistencies.
Mid-20th Century: Semi-automatic Machines
In the 1950s-60s, semi-automatic machines emerge, utilizing basic mechanical components to reduce manual labor. They required human intervention for loading and unloading, albeit still more efficient than fully manual methods.
Late 20th Century: Early Automatic Systems
The late 1970s to 1980s saw the advent of early automation. Integrating simple electronics, these machines could handle higher volumes but were bulky and less reliable than desired. The rise of microprocessors marked significant improvements in control and precision.
1990s: Improved Electronics and Software
The 1990s focus on refining control systems using better sensors and software. More reliable and user-friendly interfaces were developed. The introduction of barcode technology and networking capabilities also enhanced tracking and inventory management.
Early 2000s: Automation and Integration
By the early 2000s, further integration with laboratory information systems (LIS) and robotic handling systems allowed seamless automation in clinical and research environments. Improved software allowed for greater customization and error reduction.
2010s: Advanced Robotics and AI
The 2010s experienced a surge in usability with advanced robotics, AI, and machine learning integration. Systems became more flexible, accommodating various tube sizes and shapes automatically, and included sophisticated error-detection algorithms.
Recent Developments: IoT and Smart Systems
Today, IoT-enabled devices facilitate real-time monitoring and maintenance, while cloud computing enhances data accessibility and integration with broader health informatics systems. Enhanced connectivity and modularity make modern tube labelers versatile and fit for varied applications.
The automatic tube labeler’s journey from manual to smart, connected systems reflects ongoing technological advancements, continually pushing the boundaries of efficiency and reliability in laboratory settings.
How to Select a Reliable automatic tube labeler
Selecting a reliable automatic tube labeler is a crucial decision that can impact the efficiency and accuracy of your labeling process. Here are key considerations to help you choose wisely:
1. Vendor Reputation:
– Research the manufacturer or supplier’s reputation. Look for companies with a proven track record in producing high-quality labeling equipment. Customer reviews, testimonials, and case studies can provide valuable insights.
2. Machine Specifications:
– Ensure the machine meets your specific requirements. Consider the types of tubes you need to label, the label sizes, and the speed of production. Make sure the machine can handle various tube diameters and lengths if necessary.
3. Ease of Use:
– The machine should be user-friendly with an intuitive interface. Training should be minimal, allowing operators to quickly learn and use the system efficiently.
4. Accuracy and Precision:
– Precision in label placement is critical. Check the machine’s tolerance levels for label misalignment. High accuracy ensures consistent and professional labeling.
5. Maintenance and Support:
– Assess the ease of maintenance and availability of customer support. Reliable after-sales service and readily available spare parts can minimize downtime and keep your operations running smoothly.
6. Flexibility and Compatibility:
– The machine should be adaptable to future requirements, whether it’s different tube sizes or new types of labels. Versatility can save costs in the long run.
7. Compliance and Safety:
– Ensure the labeler meets industry standards and regulations. Safety features are essential to protect operators and maintain a safe working environment.
8. Cost and ROI:
– Consider the initial investment and the long-term return on investment (ROI). A higher upfront cost may be justified by the machine’s durability, efficiency, and lower operational costs.
9. Test the Equipment:
– If possible, request a trial run or a demo. This hands-on experience can provide a clearer picture of the machine’s capabilities and suitability for your needs.
By carefully evaluating these factors, you can select a reliable automatic tube labeler that enhances your production efficiency and meets your specific labeling needs.
List “automatic tube labeler” FAQ
#### Automatic Tube Labeler FAQ
1. What is an automatic tube labeler?
An automatic tube labeler is a machine designed to apply labels to tubes efficiently and consistently. These labels can include barcodes, batch numbers, and other important information necessary for tracking and identification.
2. How does an automatic tube labeler work?
The machine uses sensors and software to detect the tube and apply a pre-printed or print-on-demand label to the designated area on the tube. The process is automated, reducing manual labor and errors.
3. What types of tubes can it label?
Automatic tube labelers can typically handle a variety of tube types including microcentrifuge tubes, blood collection tubes, and PCR tubes. Compatibility may vary by model.
4. What are the benefits of using an automatic tube labeler?
– Efficiency: Speeds up the labeling process.
– Accuracy: Reduces human errors.
– Consistency: Produces uniform labels every time.
– Traceability: Ensures that all tubes are properly identified, aiding in laboratory management and compliance.
5. Can the machine handle different sizes of labels?
Yes, most automatic tube labelers are adjustable and can handle various label sizes, but it’s essential to verify this feature with the specific model.
6. What is the typical labeling speed?
Labeling speed varies by model but generally ranges from a few hundred to several thousand tubes per hour.
7. Is the equipment difficult to set up and use?
Most models are user-friendly with intuitive controls. Initial setup often involves loading the labels, calibrating the machine, and adjusting the settings for specific tube types.
8. What maintenance is required?
Regular maintenance involves cleaning the sensors, checking for label jams, and periodically servicing the mechanical parts to ensure optimal performance.
9. Are there software requirements?
The machine usually comes with proprietary software for design and management of labels, often compatible with existing laboratory information management systems (LIMS).
10. What should I consider before purchasing?
Consider the types of tubes you need to label, the required throughput, compatibility with your existing systems, and the machine’s adaptability to future needs. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to ensure the investment meets your operational goals.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about automatic tube labeler for Buyer Sourcing from China
Sure, here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQs) with their answers about sourcing automatic tube labelers from China:
1. What is the lead time for delivery?
– Generally, the lead time ranges from 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the machine and current manufacturing schedules.
2. What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ)?
– Most manufacturers require a MOQ of one unit for automatic tube labelers, though bulk purchasing may offer better pricing and terms.
3. Can the labeler accommodate different tube sizes?
– Yes, most machines come with adjustable settings to handle various tube diameters and lengths. Ensure you specify your requirements upfront.
4. Are warranties and after-sales service included?
– Typically, a one-year warranty is provided. Confirm if the supplier offers local technical support or remote assistance for troubleshooting.
5. Is customization available?
– Customization options are usually available, including software tweaks and hardware adjustments to fit specific needs. Discuss details during the inquiry phase.
6. What are the payment terms?
– Common payment terms include a 30% deposit with the balance paid before shipment. Some suppliers may offer letters of credit or other financing options.
7. How do you handle shipping and import duties?
– Shipping is generally FOB (Free on Board) from the Chinese port. Buyers are responsible for freight, insurance, and customs duties upon arrival.
8. What certifications do the machines have?
– Ensure the labeler has necessary certifications like CE, ISO9001, or others required for your market. Verification is crucial for compliance and safety.
9. How is the machine quality ensured?
– Quality is typically managed through rigorous testing, quality controls, and certification compliance. Ask for references or case studies to verify quality.
10. Do you provide training for operating the machine?
– Many suppliers offer training materials, online tutorials, or even on-site training depending on the complexity of the equipment and buyer’s needs.
By addressing these common concerns, you can make a more informed decision when sourcing automatic tube labelers from China.