List Technical Parameters of “automatic packing machine”
An automatic packing machine is an advanced piece of equipment designed for efficiently packaging products with minimal human intervention. The technical parameters provide insight into its capabilities, operation, and suitability for different applications. Key parameters include:
1. Production Speed: Capacity measured in packages per minute (PPM). It varies depending on the product type and packaging material.
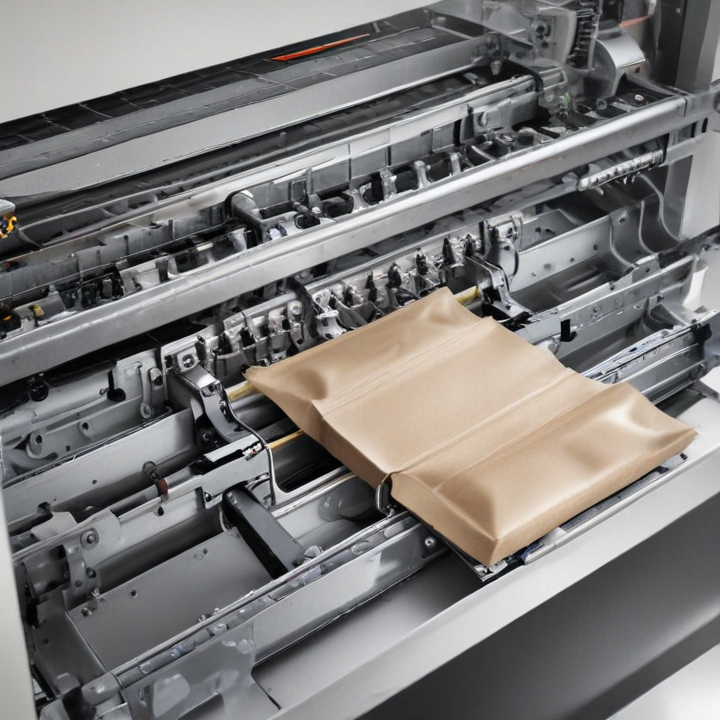
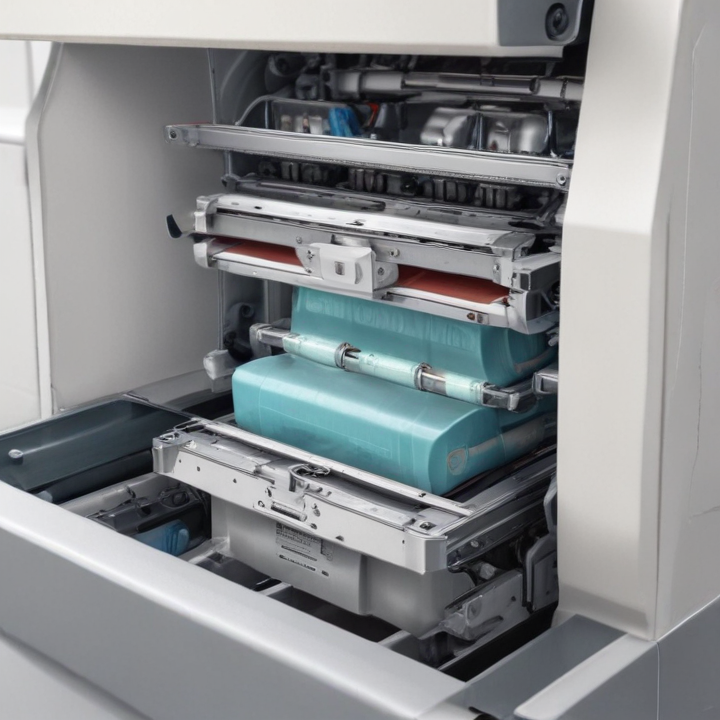
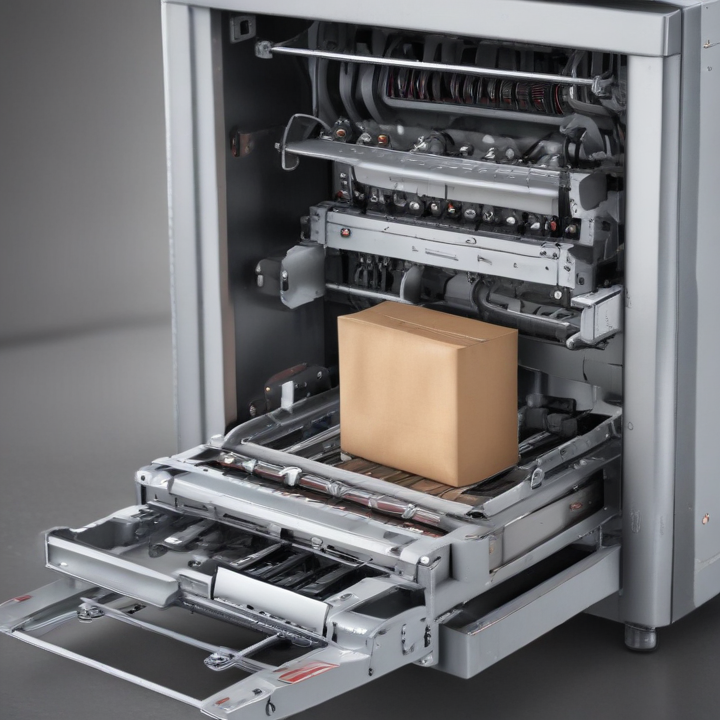
2. Packaging Types: Supports various packaging forms such as vacuum packs, sachets, pouches, cartons, or bottles. Specific models cater to particular packaging requirements.
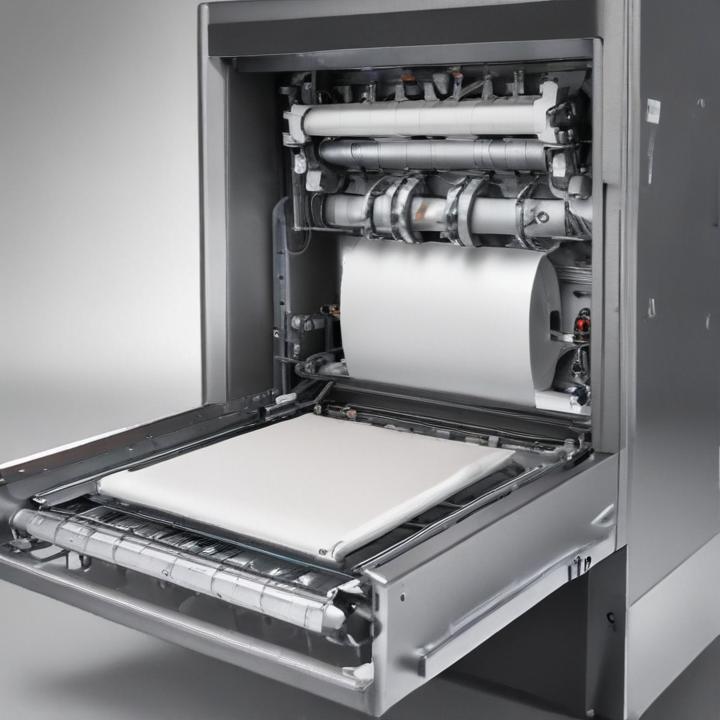
3. Material Compatibility: Compatibility with various packaging materials like plastic film, paper, aluminum foil, or laminates.
4. Filling Volume Range: Defines the minimum and maximum volume (or weight) the machine can dispense, which is crucial for different product sizes.
5. Machine Dimensions and Weight: Overall size and weight, impacting floor space requirements and mobility.
6. Power Requirements: Electrical specifications such as voltage, phase, and frequency (e.g., 220V, 1 phase, 50/60 Hz).
7. Air Supply: For machines that require pneumatic components, the air pressure and consumption rate (measured in bars or PSI and CFM).
8. Control System: Interface type, often including a touch screen, PLC (Programmable Logic Controller), and options for integration with existing systems.
9. Accuracy: Tolerance in filling volume or weight, typically noted as a percentage or gram range.
10. Sealing Mechanism: Type of seal (e.g., heat seal, ultrasonic seal) and sealing strength, important for package integrity.
11. Dimension of Package: The allowable range for package (or product) dimensions the machine can handle.
12. Operating Environment: Suitable temperature and humidity ranges for optimal machine operation.
13. Material Dosing System: Type and mechanism, such as auger, volumetric, or vacuum dosing for precise material dispensation.
14. Automation Level: Degree of automation including levels of manual intervention required, sensors, and feedback systems for error detection and correction.
15. Maintenance Requirements: Frequency and type of maintenance tasks required for optimal performance and longevity.
These parameters are crucial for selecting the right automatic packing machine tailored to specific industrial needs.
List Product features of “automatic packing machine”
Certainly! Here are the product features of an “automatic packing machine”:
1. Automation: Fully automated functions reduce the need for manual intervention, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
2. High-Speed Packaging: Capable of packaging a large number of units per minute to meet high-volume production needs.
3. Versatile Packaging Styles: Supports various packaging styles such as bags, pouches, cartons, and bottles, catering to multiple industries.
4. Precision and Accuracy: Advanced sensors and controls ensure precise packaging, reducing waste and maintaining consistent quality.
5. User-Friendly Interface: Touchscreen display and intuitive controls facilitate easy operation and customization of packing parameters.
6. Customizable Settings: Programmable settings allow adjustment of packing speed, size, and type to suit different products and requirements.
7. Integration Capabilities: Compatible with other systems like conveyors, labeling machines, and printers for streamlined production lines.
8. Durable Construction: Built with high-quality materials such as stainless steel for long-lasting performance and resistance to corrosion.
9. Energy Efficiency: Designed to consume less power while maintaining optimal performance, reducing operational costs.
10. Safety Features: Equipped with safety guards, emergency stops, and compliance with industry safety standards to protect operators.
11. Minimal Downtime: Easy maintenance and quick-change components minimize downtime and keep the machine running smoothly.
12. Compact Design: Space-efficient design allows easy integration into existing production lines without requiring extensive floor space.
13. Remote Monitoring and Control: Some models offer IoT and remote access features for real-time monitoring and troubleshooting.
14. Multi-Language Support: Interface available in multiple languages to cater to global markets.
15. Environmentally Friendly: Designed to minimize waste and energy consumption, contributing to sustainable operations.
These features make automatic packing machines an essential asset for modern manufacturing and packaging operations, tailored to enhance efficiency, precision, and overall productivity.
List Application of “automatic packing machine”
Automatic packing machines play a crucial role in various industries by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and consistency in packaging processes. Here are some key applications:
1. Food and Beverage Industry: Automatic packing machines are widely used for packaging snacks, cereals, dairy products, beverages, and frozen foods. They ensure hygienic and quick packaging, extending the shelf life of products.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry: These machines are essential for packing tablets, capsules, powders, and liquid medications. They provide precise dosing and secure packaging to maintain product integrity and avoid contamination.
3. Cosmetics and Personal Care: Automatic packing machines are used for filling and packing creams, lotions, shampoos, and other personal care products in various container types, ensuring tamper-proof and attractive packaging.
4. Chemical Industry: These machines handle the packaging of chemicals, fertilizers, and pesticides, ensuring safe, and precise measures. They also deal with corrosive and hazardous materials by providing secure packaging solutions.
5. Agriculture: Packaging seeds, grains, fertilizers, and animal feed is streamlined using automatic packing machines, ensuring accurate quantities and reducing manual labor.
6. Retail and E-commerce: Automatic packing machines help in efficiently handling large volumes of orders by packing goods in boxes, padded mailers, or polybags, and adding shipping labels swiftly.
7. Automotive and Electronics: Parts, components, and delicate electronics are securely packed using automatic machines, reducing damage during transit and improving inventory management.
8. Textiles and Apparel: From socks to fully assembled garments, these machines pack products in polybags or cartons, assisting in better presentation and protection.
9. Hardware and Tools: Automatic packing machines handle the packaging of screws, bolts, nails, and other small hardware components, ensuring sorted and quantity-specific packages.
Overall, automatic packing machines add value by improving packaging speed, reducing labor costs, and enhancing overall product safety and consistency across various sectors.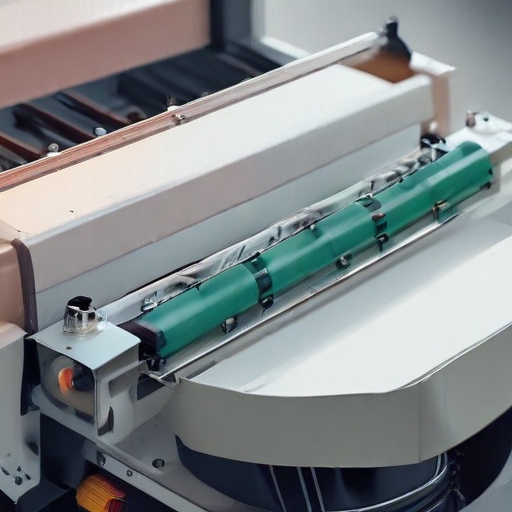
List Various Types of “automatic packing machine”
Certainly! Here are various types of automatic packing machines:
1. Flow Wrapping Machines:
– Wrap products in a continuous motion. Common in food industries, like candy bars and baked goods.
2. Vacuum Packing Machines:
– Remove air before sealing, preserving the freshness of perishable products like meats, cheeses, and vegetables.
3. Form-Fill-Seal Machines (FFS):
– Automatically form packages, fill them with product, and seal them. Used for snacks, liquids, and powders.
4. Blister Packaging Machines:
– Encase products like pharmaceuticals and small hardware in a pre-formed plastic blister.
5. Shrink Wrapping Machines:
– Enclose products in shrink film, which is then heated to form a tight seal. Useful for bundling items and providing tamper resistance.
6. Cartoning Machines:
– Automatically erect cartons, fill them with products, and seal them. Ideal for boxed items like cereals and detergents.
7. Labeling Machines:
– Apply labels automatically to bottles, cans, and other containers. Essential in industries requiring product identification and branding.
8. Palletizing Machines:
– Stack and organize boxes or packages onto pallets. Used in large-scale distribution centers and warehouses.
9. Stretch Wrapping Machines:
– Use stretchable plastic film to secure loads on pallets, providing stability during transportation.
10. Stick Pack and Sachet Packing Machines:
– Create small, single-serve packets. Popular in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetics industries for products like sugar, salt, and shampoo.
11. Auger Filling Machines:
– Specialized for filling powders and granular items into containers or pouches.
12. Liquid Filling Machines:
– Designed for filling containerized liquids such as beverages, oils, and creams.
13. Seed Counting and Packing Machines:
– Count small items (like seeds) precisely and package them. Used in the agricultural sector.
14. Bottling Machines:
– Fill, cap, and label bottles in industries like beverages, chemicals, and personal care products.
Each type of machine is designed for specific packaging needs, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring product integrity.
Custom Manufacturing Options for automatic packing machine
Custom manufacturing options for an automatic packing machine are crucial for meeting specific business needs and maximizing efficiency. Here are some key customizable features:
1. Packaging Types: Machines can be tailored to handle various packaging formats—such as pouches, cartons, bottles, or blister packs—depending on the product.
2. Material Compatibility: Adjustments can be made to accommodate different packaging materials (plastic, paper, composite films) ensuring optimal performance and durability.
3. Speed and Throughput: Customizing the speed and throughput capabilities allows the machine to match the production rate of other machinery, ensuring seamless integration into existing workflows.
4. Size and Shape Adaptability: Machines can be designed to handle different product sizes and shapes, providing flexibility for a diverse product range.
5. Automation Level: From semi-automated to fully automated systems, the level of automation can be configured to align with the available workforce and operational complexity.
6. Integration with Upstream/Downstream Processes: Custom solutions can include compatibility with upstream (filling, sealing) and downstream (labeling, palletizing) equipment for a cohesive assembly line.
7. Quality Control Systems: Incorporating vision systems or weight checks ensures every package meets quality standards, reducing waste and enhancing customer satisfaction.
8. User Interface and Software: Customizable user interfaces and control software allow for easier operation and quicker adjustments, improving user experience and productivity.
9. Environmental Controls: Machines can be outfitted to maintain specific environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) necessary for sensitive products.
10. Safety Features: Tailored safety mechanisms protect workers and comply with regulatory standards, reducing the risk of accidents.
11. branding & Aesthetics: Custom branding elements or designs can be integrated into the machine to align with corporate identity.
Tailoring these features ensures the automatic packing machine meets unique operational needs, enhancing efficiency, and productivity.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “automatic packing machine”
Quality Control (QC) of Automatic Packing Machines:
1. Incoming Material Inspection: Evaluate raw materials and components for compliance with specifications.
2. In-Process Inspection: Continuously monitor manufacturing stages to ensure adherence to quality standards.
3. Functional Testing: Conduct rigorous tests on software, sensors, and mechanical parts to confirm operational efficiency.
4. Calibration: Regular calibration of sensors and actuators to maintain accuracy.
5. Final Inspection: Comprehensive reviews and performance tests of the finished machine.
6. Documentation and Traceability: Maintain detailed records of inspections, tests, and calibrations.
7. Training and Certification: Ensuring personnel are well-trained and certified in quality standards and procedures.
8. Compliance Audits: Periodic audits to ensure compliance with industry standards and regulations like ISO 9001.
Manufacturing Process of Automatic Packing Machines:
1. Design and Prototyping:
– Conceptual Design: Develop the basic design using CAD software.
– Prototype Development: Create a prototype for testing and validation.
2. Material Sourcing:
– Component Selection: Identify and procure high-quality components and materials.
– Supplier Evaluation: Ensure suppliers comply with quality standards.
3. Machining and Fabrication:
– CNC Machining: Precision machining of parts.
– Fabrication: Welding, cutting, and assembling of structural components.
4. Assembly:
– Sub-Assembly: Assemble major subsystems like the conveyor, sealing units, and control panels.
– Main Assembly: Integrate subsystems into the main structure.
5. Electrical and Software Integration:
– Wiring and Connections: Install electrical components and ensure proper connections.
– Programming: Implement and test machine software.
6. Testing and Calibration:
– Dry Run: Initial testing without packaging material.
– Full Load Testing: Testing with actual packaging material under operational conditions.
7. Finishing:
– Surface Treatment: Apply coatings or finishes for protection.
– Branding and Labeling: Add logos and necessary labeling.
8. Quality Assurance:
– Final Review: Ensure the machine meets all specifications before shipment.
– Customer Validation: Conduct acceptance testing with the customer, if applicable.
By adhering to rigorous quality control and systematic manufacturing processes, the reliability and efficiency of automatic packing machines can be ensured.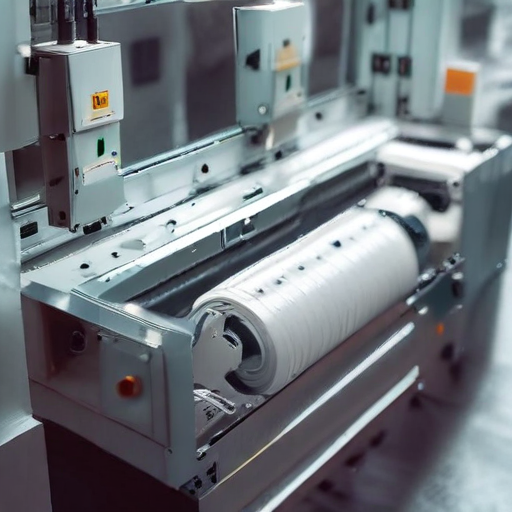
How to use “automatic packing machine”
An automatic packing machine streamlines the packaging process, efficiently handling tasks such as filling, sealing, and labeling. Here’s a step-by-step guide on operating one:
1. Setup and Preparation:
– Read the Manual: Familiarize yourself with the machine’s specific settings and requirements.
– Power Up: Ensure the machine is correctly connected to a power source.
– Materials Loading: Load the packaging materials (e.g., bags, films) into the designated holders.
– Product Loading: Ensure the product to be packed is ready and appropriately placed in the machine’s input area or hopper.
2. Configuration:
– Set Parameters: Adjust the machine settings, such as bag size, fill quantity, sealing temperature, and speed. These can usually be set via a control panel.
– Calibration: Calibrate the machine if necessary to ensure accuracy in weight and volume for each package.
3. Operation:
– Start the Machine: Press the start button to begin the packaging process.
– Monitor Performance: Keep an eye on the machine to ensure it is operating correctly. Watch for any jams or errors.
– Automatic Processes: The machine will automatically fill, seal, and cut the packaging material. Some machines may also print labels or add dates.
4. Maintenance and Safety:
– Regular Checks: Periodically check for wear and tear, clean the machine parts, and ensure no material residues remain.
– Emergency Protocol: Know how to stop the machine quickly in an emergency. Most machines have an emergency stop button.
5. Troubleshooting:
– Error Messages: Follow the troubleshooting guide in the manual for common error messages or issues.
– Technical Support: Contact the manufacturer for support if you encounter persistent issues.
Note: Always adhere to safety guidelines and wear appropriate protective gear.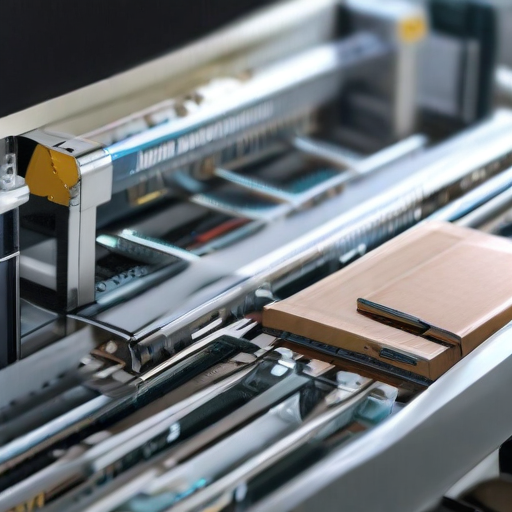
List Properties and Terms of “automatic packing machine”
An automatic packing machine is a sophisticated piece of equipment designed to streamline the packaging process in various industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. Here are some key properties and terms associated with automatic packing machines:
Properties:
1. Automation: Capable of performing repetitive tasks with minimal human intervention.
2. Speed: High-speed operation, often measured in packs per minute (PPM).
3. Accuracy: Ensures precise measurements and consistent packaging quality.
4. Versatility: Able to handle various types of packaging materials and product forms.
5. Durability: Constructed from high-quality materials for long-term operation.
6. User Interface: Often includes touch screens and programmable logic controllers (PLCs).
7. Integration: Compatible with other production line machinery for a seamless workflow.
Terms:
1. Form-Fill-Seal (FFS): A machine that forms the package, fills it with the product, and seals it in a continuous process.
2. Vertical Form-Fill-Seal (VFFS): Specifically designed to create vertical packages, often used for snacks and grains.
3. Horizontal Form-Fill-Seal (HFFS): Creates horizontal packages, ideal for items like cookies or medical devices.
4. Blister Packaging: A form of packaging used primarily for pharmaceuticals, where the product is sealed in pre-formed plastic.
5. Flow Wrapping: A process where products are wrapped in a continuous film and then sealed.
6. Shrink Wrapping: Involves wrapping a product in a plastic film that shrinks when heat is applied.
7. Labeling: The machine may include a labeling function to apply identification tags or barcodes.
8. Tray Sealing: Seals products in pre-formed trays, often used in the food industry.
9. Vacuum Sealing: Removes air from the package before sealing to prolong shelf life.
10. Weighing: Integrated weighing systems to ensure products meet specified weight criteria.
These properties and terms provide a comprehensive overview of what to expect from an automatic packing machine, highlighting its importance in modern packaging operations.
List The Evolution history of “automatic packing machine”
The evolution of automatic packing machines has been transformative, driven by the need for efficiency, precision, and labor optimization. Here is a brief history:
1. Early Manual Packing (Pre-1900s): Packaging was largely manual, involving basic tools and significant human labor. Little to no automation existed.
2. Industrial Revolution (Late 1800s – Early 1900s): The onset of the Industrial Revolution introduced rudimentary mechanization. Machines began automating simple tasks like sealing and labeling. The first notable mechanized equipment emerged in this period.
3. First Automatic Packing Machines (1920s-1930s): Introduction of the first automatic filling machines for products like grains and powders. Developments in electrical engineering facilitated control systems, enhancing operational efficiency.
4. Post-World War II Expansion (1940s-1950s): Continued advancements in electronics and materials led to more sophisticated packing machines. The consumer boom increased demand for packaged goods, accelerating innovation in automatic packing technologies.
5. Microprocessors and PC-Controlled Packing (1970s-1980s): Integration of microprocessors improved machine accuracy and flexibility. The first computer-controlled packing machines emerged, offering programmable packaging operations.
6. Advanced Robotics and Sensors (1990s): The advent of robotics and advanced sensors allowed for greater precision and automation, reducing human intervention. Vision systems were introduced for quality control.
7. Internet of Things (IoT) and Smart Packing (2000s – Present): IoT technologies have enabled smart packing machines capable of real-time monitoring and diagnostics. Modern systems involve machine learning and AI for predictive maintenance and efficiency optimization.
8. Sustainability and Advanced Materials (2020s): Focus on sustainable packaging materials and energy-efficient machines to meet environmental standards. Automation has expanded across various industries, including food, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
The journey from manual to highly sophisticated automatic packing systems marks significant technological strides, reflecting broader trends in industrial automation and smart manufacturing.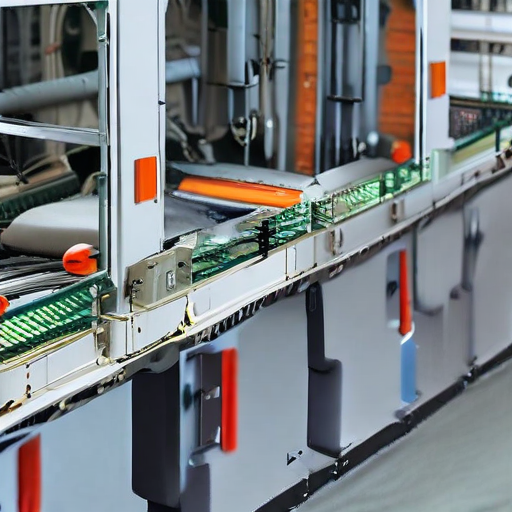
How to Select a Reliable automatic packing machine
Selecting a reliable automatic packing machine involves careful consideration of several factors to ensure that the machine meets your specific needs and offers good performance. Here are key steps to guide your decision:
1. Define Your Requirements: Identify the type of products you need to pack (e.g., liquids, solids, powders) and the packaging style (e.g., bottles, pouches, cartons). Consider the production capacity, speed, and automation level you require.
2. Research Manufacturers: Look for established manufacturers with a good reputation in the market. Check their experience, product range, and customer reviews. Reliable companies often provide better support and service.
3. Evaluate Quality and Reliability: Assess the build quality, materials used, and reliability of the machine. High-quality components generally translate to better performance and longevity. Ask for references or case studies from existing customers.
4. Check for Compliance and Certifications: Ensure the machine complies with industry standards and certifications relevant to your sector (e.g., FDA for food and pharmaceuticals).
5. Consider Technology and Features: Modern packing machines come with various features like touch-screen controls, integration with other systems (e.g., ERP, MES), and IoT capabilities. Choose one that aligns with your technical needs.
6. Assess Ease of Use and Maintenance: A user-friendly machine reduces downtime and training costs. Ensure spare parts are readily available and evaluate the manufacturer’s support and maintenance services.
7. Cost and ROI: Compare the price against the features and expected return on investment. Sometimes, spending a bit more initially results in better long-term savings due to higher efficiency and lower maintenance costs.
8. Request Demos and Trials: If possible, see the machine in action. Request a demo or trial to ensure it handles your product efficiently and meets your expectations.
By focusing on these aspects, you can select a reliable automatic packing machine that enhances productivity and delivers consistent performance.
List “automatic packing machine” FAQ
Automatic Packing Machine FAQ
1. What is an automatic packing machine?
– An automatic packing machine is a device designed to handle the packaging process of products with minimal human intervention. It automates tasks such as filling, sealing, labeling, and coding.
2. What types of products can it pack?
– Automatic packing machines can handle a wide variety of products, including solids, liquids, powders, and granules. Specific designs cater to different product types and packaging materials.
3. How do I choose the right machine for my needs?
– Consider factors like the type of product, packaging material, speed requirements, production volume, and budget. Consulting with manufacturers or industry experts can provide valuable insights.
4. What are the benefits of using an automatic packing machine?
– Increased efficiency, consistent packaging quality, reduced labor costs, enhanced production speed, and minimized manual errors.
5. How difficult is it to operate and maintain?
– Modern machines come with user-friendly interfaces and can be operated with minimal training. Regular maintenance, as per the manufacturer’s guideline, ensures longevity and optimal performance.
6. What is the typical cost?
– The cost varies widely depending on the machine’s complexity, capacity, and features. Basic models may start in the low thousands, while high-end systems can run into hundreds of thousands of dollars.
7. Do these machines comply with industry regulations?
– Reputable manufacturers ensure their machines meet industry standards and regulations. It’s important to verify compliance, especially for food, pharmaceutical, and other regulated sectors.
8. Can I get customization for specific needs?
– Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to tailor the machine to specific requirements, including product type and packaging style.
9. How does product changeover work?
– Many modern machines are designed for quick and easy product changeovers with minimal downtime, utilizing programmable settings and modular components.
10. What support and training are available?
– Manufacturers typically provide training, documentation, and ongoing support. Some offer remote assistance and regular maintenance services to ensure smooth operation.
By understanding these common questions, one can better evaluate and integrate an automatic packing machine into their production line efficiently.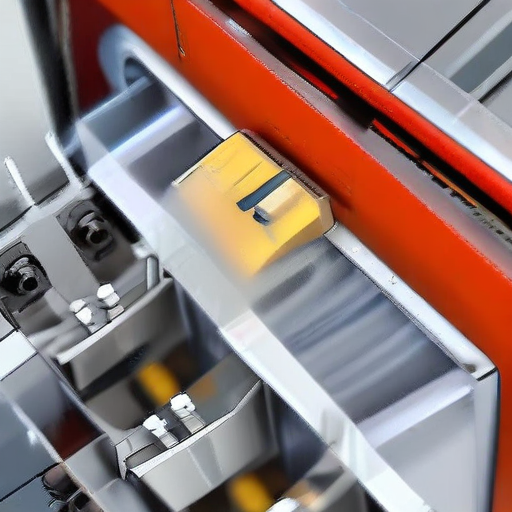
Top 10 FAQ with answer about automatic packing machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What is an automatic packing machine?
An automatic packing machine is equipment that automates the packing process by forming, filling, sealing, and sometimes labeling or coding the packaging. It improves efficiency, reduces manual labor, and ensures consistency in packaging.
2. What types of products can be packed by an automatic packing machine?
Automatic packing machines can handle a variety of products, including powders, granules, liquids, semi-liquids, and solids. They are used across industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and hardware.
3. What are the different types of automatic packing machines available in China?
Common types include vertical form fill seal (VFFS) machines, horizontal form fill seal (HFFS) machines, sachet packing machines, blister packing machines, and vacuum packing machines.
4. What is the average lead time for an automatic packing machine from China?
Lead times can vary based on the complexity and customization required, typically ranging from 30 to 90 days. It’s important to confirm the lead time directly with the supplier.
5. How do I ensure the quality of the machine when sourcing from China?
Ensure quality by selecting reputable suppliers, reviewing certifications like ISO, CE, or FDA, and requesting product samples or visiting facilities. Engaging third-party inspection services can also help verify quality before shipment.
6. What technical support and after-sales service can I expect?
Reputable suppliers often provide detailed manuals, video tutorials, remote support, and on-site engineer services. Ensure the supplier offers adequate spare parts and a warranty period, typically between 1-2 years.
7. What are the costs involved with purchasing an automatic packing machine from China?
Costs include the price of the machine, shipping, customs duties, installation, and training. Always request a detailed quotation that includes all possible expenses to avoid surprises.
8. How do I handle the importation of an automatic packing machine?
You need to work with a customs broker to clear the machine through customs. Make sure to have all necessary documentation, including invoices, packing lists, and certificates of origin.
9. Can the machine be customized to fit my specific packing needs?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to fit specific product requirements, such as altered machine dimensions, customized molds, or specialized features for unique packaging.
10. What should I look for in terms of machine safety and certifications?




