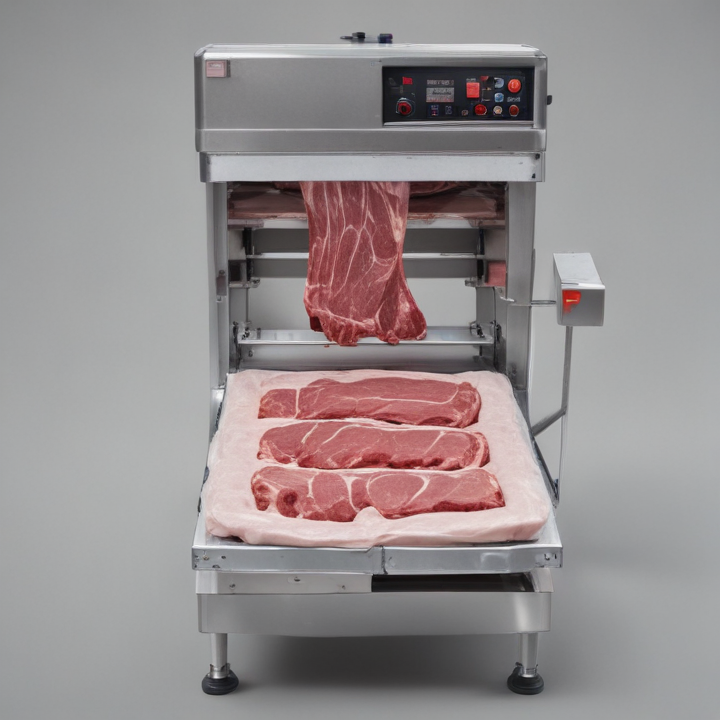
List Technical Parameters of “meat packaging machine”
Certainly! Here are some key technical parameters of a meat packaging machine:
1. Capacity: Represents the throughput of the machine, usually measured in packages per hour or kilograms per hour.
2. Machine Dimensions: Length, width, and height, important for space planning and integration into production lines.
3. Weight: Total weight of the machine, which affects transportation and installation procedures.
4. Material Compatibility: Types of materials that can be used for packaging, such as plastic, vacuum bags, or tray materials.
5. Power Supply: Voltage, frequency, and power consumption details, vital for electrical requirements.
6. Sealing Type: Types of seals the machine can create, such as heat seal, vacuum seal, or modified atmosphere packaging (MAP).
7. Control System: Type of control system used—manual, semi-automatic, or fully automatic—with possible integration with PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers).
8. Temperature Range: The range of temperatures the machine can operate at for sealing or maintaining product integrity.
9. Speed Adjustment: Ability to adjust packaging speed according to requirements.
10. Material Usage: Information on the consumption rate of packaging material.
11. Precision: Accuracy in cutting and sealing to ensure uniform package sizes and minimize waste.
12. Hygiene Standards: Compliance with food safety and hygiene norms like FDA or EU food safety regulations.
13. Maintenance Requirements: Frequency and ease of routine maintenance operations, affecting downtime and operational efficiency.
14. Automation Level: Features like automatic feeding, filling, sealing, and labeling, indicating the overall efficiency of the machine.
15. Operational Noise Level: Noise output during operation, important for worker safety and comfort.
16. Vacuum Pressure: For vacuum packaging machines, the level of vacuum pressure achievable, usually measured in millibars or Pascals.
17. Accessories: Availability of additional components like conveyors, printers, and weighing systems that enhance functionality.
By considering these parameters, you can make an informed decision on the suitability of a meat packaging machine for your specific requirements.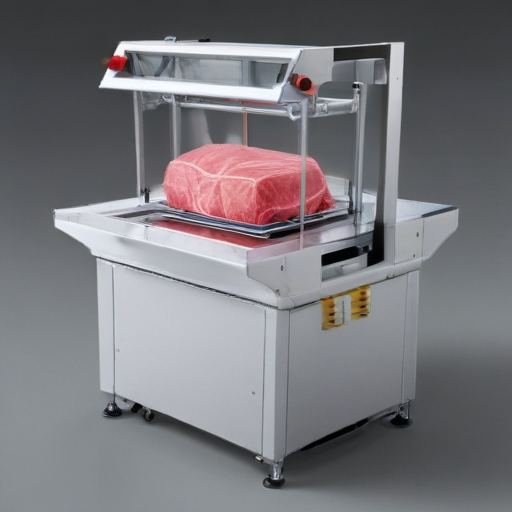
List Product features of “meat packaging machine”
Sure, here are the features of a “meat packaging machine” concisely listed:
1. Automation: Fully automated operation for swift and efficient packaging.
2. Versatility: Capable of handling various types and cuts of meat, including ground, sliced, and whole pieces.
3. High-Speed Performance: Fast processing speeds to meet high demand, ensuring high throughput.
4. Vacuum Sealing: Advanced vacuum sealing technology to extend shelf life and maintain product freshness.
5. Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP): Options to use gas flushing techniques to preserve the meat color and quality.
6. Temperature Control: Built-in systems to keep the meat at optimal temperatures during packaging.
7. Hygiene and Safety: Easy-to-clean surfaces and components to comply with strict food safety regulations.
8. Durable Materials: Made from stainless steel and other durable materials to withstand harsh conditions and frequent use.
9. User-Friendly Interface: Intuitive touch-screen controls and programmable settings for ease of operation.
10. Size Adjustability: Adjustable components to accommodate different package sizes and types.
11. Consistent Sealing: Reliable sealing mechanisms to prevent leaks and ensure package integrity.
12. Integration Capabilities: Can be integrated with existing production lines and other equipment like labeling and weighing machines.
13. Energy Efficiency: Designed for low energy consumption to reduce operational costs.
14. Smart Monitoring: Equipped with sensors and software for real-time monitoring and diagnostics.
15. Compliance: Meets regulatory standards for food processing and packaging.
These features collectively ensure that the meat packaging machine delivers efficient, safe, and high-quality packaging solutions.
List Application of “meat packaging machine”
Meat packaging machines play a crucial role in the food industry, ensuring that meat products are preserved, protected, and presented in an optimal manner. Here are some key applications:
1. Extended Shelf Life: Vacuum packaging and modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) remove air and replace it with gases that inhibit bacterial growth, thereby extending the shelf life of meats.
2. Hygiene and Safety: Packaging machines are designed to meet stringent sanitation standards, minimizing the risk of contamination and ensuring food safety for consumers.
3. Portion Control: These machines can be configured to pack specific quantities, streamlining distribution and retail operations by providing consistent and manageable portions.
4. Enhanced Product Aesthetics: Professional packaging enhances the appearance of meat products, making them more appealing to consumers, which can drive sales.
5. Branding and Information: Machines can be equipped to label packages with brand information, nutritional facts, expiration dates, and cooking instructions, helping consumers make informed purchasing decisions.
6. Cost Efficiency: Automated packaging reduces labor costs and increases efficiency, allowing for high-speed operations that can handle large volumes of product with minimal human intervention.
7. Waste Reduction: By precisely measuring and packaging meat, these machines help reduce waste in both the processing plant and the end user’s household.
8. Preservation of Quality: Meat packaging machines help maintain the texture, flavor, and nutritional value of meat by protecting it from environmental factors such as UV light, moisture, and temperature fluctuations.
9. Regulatory Compliance: Automated systems ensure that packaging meets legal standards and regulations, assisting manufacturers in adhering to local and international guidelines.
10. Transport Efficiency: Proper packaging ensures that meat products can withstand the rigors of transportation without spoilage or damage, thus reaching retailers and consumers in optimal condition.
In summary, meat packaging machines are integral to the meat industry, providing benefits ranging from extended shelf life and enhanced safety to improved cost efficiency and waste reduction.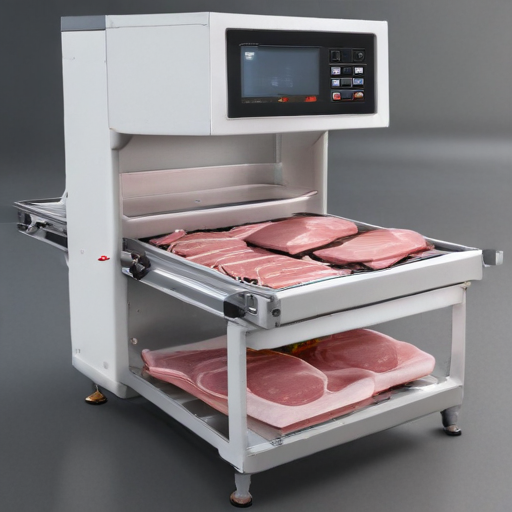
List Various Types of “meat packaging machine”
There are several types of meat packaging machines, each designed to meet specific packaging requirements for various kinds of meat products. Here are some common types:
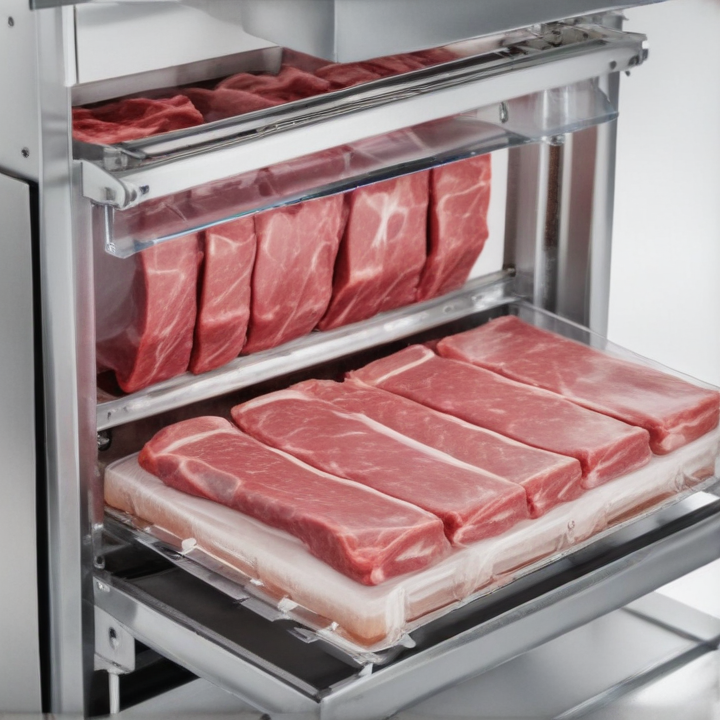
1. Vacuum Packaging Machines: These machines remove air from the package to extend the shelf life of the meat. They are ideal for preserving freshness and preventing freezer burn. Types include chamber vacuum sealers, external vacuum sealers, and double sealers.
2. Tray Sealers: Used for sealing trays filled with meat, typically with a plastic film. Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP) tray sealers can also be used to extend shelf life by replacing oxygen with gases like nitrogen.
3. Thermoforming Machines: These machines form packages from rolls of film, fill them with meat, and then seal them. They are common for both vacuum and MAP applications.
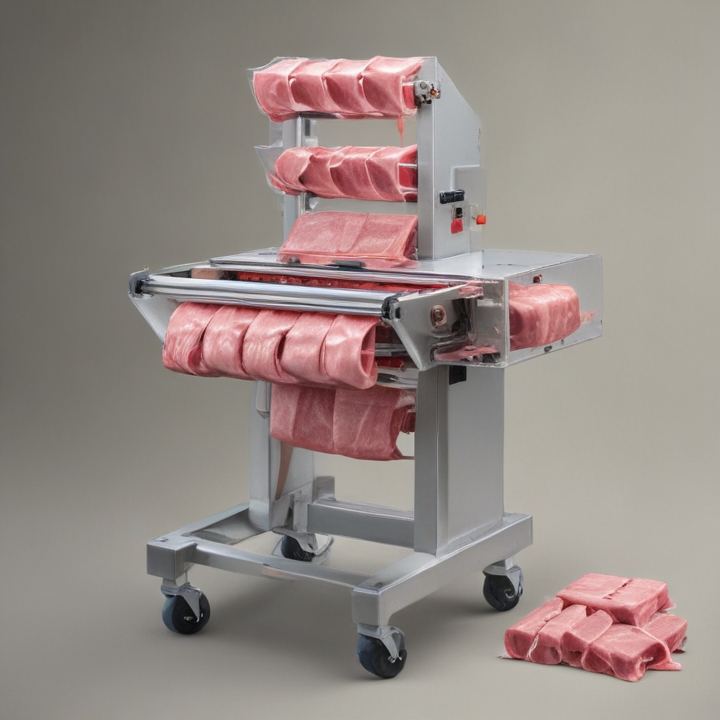
4. Flow Wrapping Machines: Flow wrappers wrap meat products in a continuous film, which is sealed at the edges. This is suitable for products like sausages or hot dogs.
5. Horizontal Form Fill Seal (HFFS) Machines: These machines form packages from a roll of film, fill them with meat, and then seal them all in a horizontal process. These are versatile machines used for various meat products.
6. Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS) Machines: Similar to HFFS but oriented vertically, these machines are often used for ground meats or smaller pieces of meat.
7. Overwrapping Machines: These machines wrap meat trays with a stretch film, commonly used in retail applications. They ensure a tight, aesthetically pleasing seal and are typically used for fresh meat.
8. Vacuum Skin Packaging (VSP) Machines: These machines apply a skin-tight layer of film over the meat, which adheres to the product contours and the tray. This method enhances visual appeal and product shelf life.
9. Slicing and Portioning Machines: Though not exactly packaging machines, these devices are often integrated into packaging lines to slice meats into uniform portions before packaging.
Each type of machine serves specific needs based on the meat product, desired shelf life, and presentation requirements.
Custom Manufacturing Options for meat packaging machine
Custom manufacturing for meat packaging machines offers a variety of options to cater to diverse requirements. Here’s a brief overview of the customizable aspects:
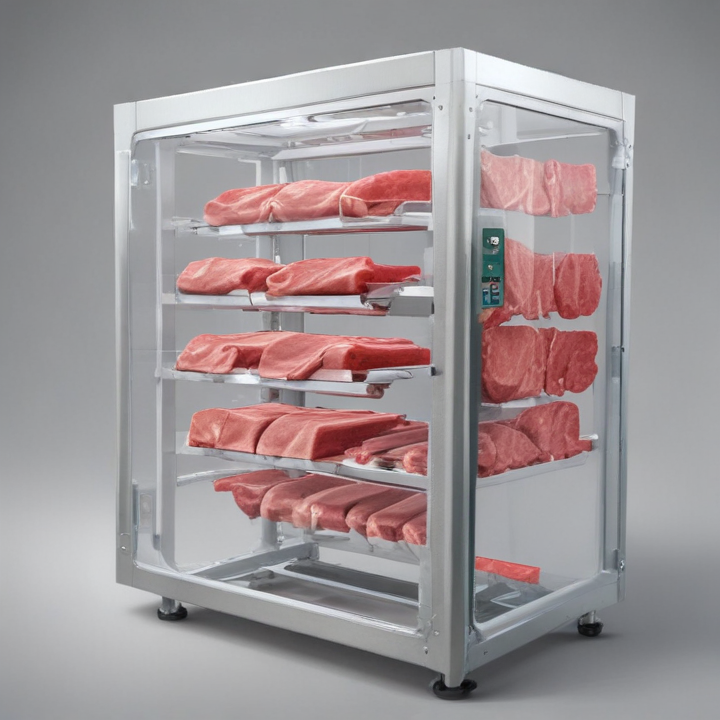
1. Size and Capacity: Machines can be tailored in size to fit spatial constraints and designed with varied throughput capacities, from small-scale operations to high-volume production lines.
2. Material Selection: Custom machines can be built using different materials to comply with hygiene standards and withstand operational stress. Common materials include stainless steel, food-grade plastics, and specialized coatings.
3. Automation Levels: Machines can be customized to different levels of automation. Options range from semi-automatic with manual adjustments to fully automated systems with minimal human intervention.
4. Pack Types: Custom equipment can handle various packaging types, including vacuum packs, shrink wraps, modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), and skin packs. Machines can be designed to switch between packaging types with ease.
5. Sealing and Cutting Mechanisms: Customizable sealing and cutting technologies including rotary, impulse, and heat-sealing to cater to different packaging materials and desired seal integrity.
6. Integration with Existing Systems: Compatibility with existing machinery and workflows is crucial. Custom machines can be designed for seamless integration with current production lines, conveyor systems, and labeling units.
7. Sanitation and Maintenance Features: Enhanced sanitation features like CIP (clean-in-place) systems, easy-to-disassemble parts, and corrosion-resistant surfaces can be incorporated to ensure regulatory compliance and ease of maintenance.
8. Control and Monitoring Systems: Advanced control panels and monitoring systems including touchscreens, IoT-enabled interfaces, and real-time data tracking can be customized to improve operational efficiency and traceability.
9. Energy Efficiency: Custom machines can feature energy-saving components and designs to reduce operational costs and environmental impact.
By tailoring these aspects, manufacturers can create highly efficient, compliant, and cost-effective meat packaging machines that enhance productivity and meet specific operational needs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “meat packaging machine”
### Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of a “Meat Packaging Machine”
#### Manufacturing Process:
1. Design and Prototyping:
– Conceptualization: Create initial design layouts and specifications.
– CAD Modeling: Develop detailed CAD models for all components.
– Prototyping: Use 3D printing or CNC machining to produce prototype parts for testing.
2. Material Selection:
– Metal Selection: Choose durable, food-safe metals like stainless steel for parts exposed to meat.
– Other Materials: procure high-quality plastics and electronic components that meet safety standards.
3. Fabrication:
– Machining: Use CNC machines to manufacture precise parts.
– Sheet Metal Work: Laser cutting, bending, and welding to create the structure.
4. Assembly:
– Component Integration: Assemble mechanical, electrical, and electronic parts.
– Subsystem Installation: Install conveyor belts, sealing systems, and cutting units.
5. Programming and Calibration:
– Software Installation: Upload control software and parameters.
– Calibration: Adjust machinery to ensure optimal performance.
6. Testing:
– Dry Run: Conduct tests without meat to verify mechanical functionality.
– Wet Run: Test with meat to ensure hygienic operation and consistency in packaging.
#### Quality Control:
1. Incoming Inspection:
– Raw Material Check: Verify quality certificates and inspect incoming materials for defects.
– Component Testing: Conduct random sampling and testing on electrical and mechanical parts.
2. In-Process Control:
– Dimensional Checks: Use precision instruments to verify part dimensions during machining.
– Functional Tests: Validate sub-assemblies like sealing units and conveyors.
– Documentation: Maintain logs of inspections and tests.
3. Final Inspection:
– Performance Testing: Run the fully assembled machine under operational conditions.
– Safety Checks: Examine electrical systems and verify compliance with food safety standards.
– Endurance Testing: Operate the machine continuously for an extended period to ensure reliability.
4. Customer Feedback and Continuous Improvement:
– Post-Delivery Monitoring: Gather data on machine performance from customers.
– Iterative Improvements: Update design and manufacturing processes based on feedback.
Through rigorous quality control and a meticulous manufacturing process, meat packaging machines are developed to ensure efficiency, safety, and reliability.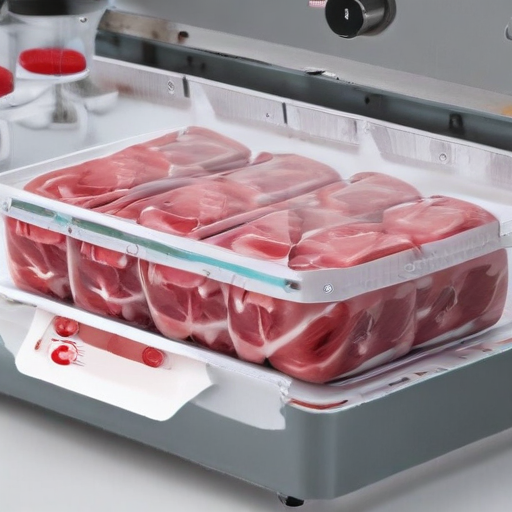
How to use “meat packaging machine”
Using a meat packaging machine involves several key steps to ensure efficiency, safety, and hygiene. Here’s a concise guide:
1. Preparation:
– Inspect the Machine: Ensure the machine is clean and in proper working condition.
– Sanitize: Wash your hands and wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
2. Setup:
– Load Packaging Material: Insert the film or packaging material according to the machine’s specifications.
– Adjust Settings: Set the desired parameters such as temperature, vacuum level, and sealing time based on the type of meat.
3. Loading Meat:
– Portion Control: Ensure meat is cut and portioned as required.
– Place Meat: Position the meat on the loading tray or conveyor belt. Ensure pieces do not overlap.
4. Operation:
– Start Machine: Turn on the machine and initiate the packaging process.
– Monitor: Keep an eye on the machine to ensure it is operating correctly. Look for issues like improper seals or misaligned packages.
5. Sealing:
– Check Seals: Make sure the seals are tight and intact to prevent spoilage.
– Repackage if Necessary: Address any improperly sealed packages immediately.
6. Post-Operation:
– Turn Off: Once packaging is complete, turn off the machine.
– Clean Up: Remove any leftover meat and clean the machine thoroughly to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination.
– Inspect Packages: Confirm that all packages are correctly sealed and labeled appropriately.
7. Storage:
– Labeling: Ensure each package is labeled with content, date, and other relevant information.
– Store: Place the packaged meat in the designated storage area, such as a refrigerator or freezer.
These steps ensure that your meat packaging process operates smoothly, safely, and efficiently, maintaining high standards of food safety and quality.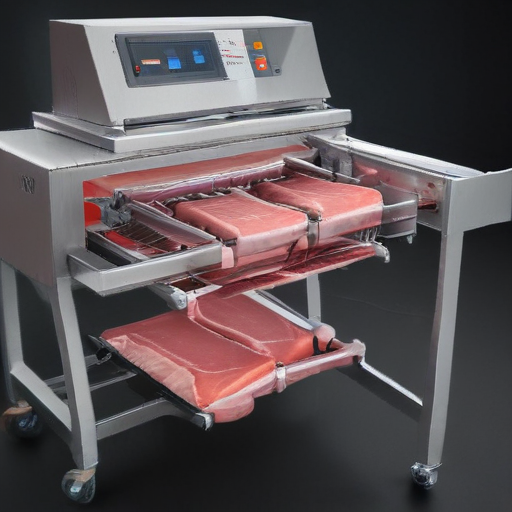
List Properties and Terms of “meat packaging machine”
Properties of Meat Packaging Machine:
1. Material Compatibility:
– Stainless Steel: Resists corrosion and complies with food safety standards.
– High-Density Plastics: Durable and safe for contact with food.
2. Automation Level:
– Manual: Requires operator intervention for most processes.
– Semi-Automatic: Partial automation with some manual tasks.
– Fully Automatic: Minimizes human intervention, increasing efficiency.
3. Packaging Types:
– Vacuum Packing: Extends shelf life by removing air.
– Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP): Uses a gas mix to preserve freshness.
– Skin Packaging: Applies a tight film over the product and tray, enhancing visibility and protection.
4. Sealing Mechanism:
– Heat Sealing: Uses heat to seal packages securely.
– Cold Sealing: Uses adhesive properties activated by pressure.
5. Size and Capacity:
– Small-scale: Suitable for small businesses or artisanal producers.
– Industrial-scale: Designed for large volume operations.
6. Hygiene and Cleanability:
– Easily disassembled parts for thorough cleaning.
– Smooth surfaces to prevent bacterial contamination.
7. Control System:
– Digital Interface: Touch screen for setting parameters.
– Mechanical Controls: Simpler, dial-based systems.
8. Speed and Efficiency:
– Measured in packages per minute (PPM).
– Influences productivity and operational costs.
Terms Associated with Meat Packaging Machines:
1. Thermoformer: A machine that forms and seals packages by applying heat and pressure to plastic.
2. Tray Sealer: Seals pre-formed trays with a top film.
3. Flow Wrapper: Wraps products in a continuous film, typically for sausages or ready-to-eat meats.
4. Vertical Form Fill Seal (VFFS): Forms bags from a roll of packaging material and fills them.
5. Horizontal Form Fill Seal (HFFS): Similar to VFFS but operates horizontally, ideal for larger pieces of meat.
6. Die-Cutting: Cuts packaging material to the desired shape and size.
7. Film Roll: The roll of packaging material used by the machine.
8. Load Cell: Devices that measure weight for portion control.
9. Gas Flushing: Introducing a mix of gases to the package to extend shelf life.
10. Label Applicators: Machines that apply labels to packaged products.
This concise outline provides a snapshot of the key properties and terms related to meat packaging machines.
List The Evolution history of “meat packaging machine”
The evolution of meat packaging machines spans several centuries, progressing from manual methods to sophisticated automated systems. Here’s a concise overview:
Early Methods:
1. Pre-Industrial Era (Before 1800s):
– Meat preservation methods included salting, smoking, and curing.
– Packaging was rudimentary, often using natural materials like leaves, animal skins, or primitive clay containers.
Industrial Revolution:
2. 19th Century:
– Introduction of tinned/canned meat, a significant breakthrough by French inventor Nicolas Appert (1810).
– Manual canning processes began to be mechanized.
Early 20th Century:
3. Early 1900s:
– Development of vacuum packaging to extend meat shelf life.
– Mechanization in meat cutting and packaging with simple assembly lines.
4. Mid 1900s:
– Emergence of automated vacuum packaging machines.
– Polyethylene film and plastic wraps introduced, offering better hygiene and visibility.
Late 20th Century:
5. 1960s-1980s:
– Evolution of modified atmosphere packaging (MAP) to maintain freshness.
– Computer-controlled systems improved precision in weighing, sealing, and labeling.
6. 1990s:
– Advancements in flexible packaging materials.
– Integration of barcode technology for tracking and inventory management.
21st Century:
7. 2000s onward:
– Adoption of robotics and advanced automation, reducing manual labor.
– Innovations in sustainable packaging materials and eco-friendly practices.
– Smart packaging technology with sensors for monitoring freshness and safety.
Current Trends:
8. 2010s-2020s:
– Enhanced focus on food safety with advanced sterilization methods.
– Integration of AI and IoT for real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance of machines.
– Customized packaging solutions to meet diverse consumer preferences.
These advancements have resulted in more efficient, safer, and environmentally conscious meat packaging solutions, reflecting the industry’s ongoing innovation trajectory.
How to Select a Reliable meat packaging machine
Selecting a reliable meat packaging machine involves several critical considerations to ensure efficiency, safety, and quality in your meat processing operations. Here are essential factors to guide you:
1. Machine Type and Capacity:
– Determine the type of packaging required (e.g., vacuum packaging, modified atmosphere packaging, skin packaging).
– Assess the daily production volume to select a machine with adequate capacity.
2. Build Quality and Material:
– Opt for machines made from stainless steel or food-grade materials to ensure durability and hygiene.
– Check for sturdy construction and reliable components.
3. Automation and Technology:
– Consider machines with automation features for sealing, cutting, and labeling to enhance efficiency.
– Evaluate the ease of use, including user-friendly interfaces and programmability.
4. Compliance and Standards:
– Ensure the machine meets relevant food safety standards (e.g., USDA, FDA, CE).
– Look for certifications that indicate compliance with industry regulations.
5. Brand Reputation and Reviews:
– Research reputable brands known for quality and reliability.
– Read customer reviews and testimonials to gauge user satisfaction.
6. Maintenance and Support:
– Check the availability of technical support and the manufacturer’s warranty.
– Inquire about the ease of maintenance and availability of spare parts.
7. Cost-Effectiveness:
– Balance initial costs with long-term benefits such as energy efficiency, reduced waste, and operational savings.
– Consider potential ROI through increased productivity and product shelf-life.
8. Customization and Flexibility:
– Ensure the machine can handle various packaging sizes and types to accommodate diverse product lines.
– Look for adjustable settings to adapt to different packaging requirements.
By factoring in these considerations, you can select a reliable meat packaging machine that meets your operational needs and ensures the quality and safety of your meat products.
List “meat packaging machine” FAQ
### Meat Packaging Machine FAQ
Q1: What types of meat can be packaged using these machines?
A1: Meat packaging machines can handle various types of meat, including beef, pork, chicken, fish, and processed meats like sausages and deli cuts.
Q2: What are the common types of meat packaging machines?
A2: Common types include vacuum sealers, thermoforming machines, tray sealers, and flow wrap machines.
Q3: How does a vacuum sealer work?
A3: A vacuum sealer removes air from the package and seals it, extending the shelf life by reducing oxidation and bacterial growth.
Q4: Can these machines handle different packaging materials?
A4: Yes, meat packaging machines are compatible with various materials, such as plastic, film, and aluminum.
Q5: What is the importance of Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)?
A5: MAP extends the shelf life by modifying the atmosphere inside the package, usually by reducing oxygen and increasing nitrogen or carbon dioxide levels.
Q6: Are meat packaging machines easy to clean?
A6: Most machines are designed with hygiene in mind, featuring easy-to-clean surfaces and components to meet food safety standards.
Q7: How do I choose the right machine for my needs?
A7: Consider factors like the type of meat, desired packaging style, production speed, and budget. Consulting with manufacturers can provide tailored solutions.
Q8: How fast can these machines package meat?
A8: Speed varies by machine type and model, ranging from a few dozen to several hundred packages per minute.
Q9: Do these machines require skilled operators?
A9: Basic operation may require minimal training, but achieving optimal performance often necessitates skilled personnel or supervisors.
Q10: What is the typical cost of a meat packaging machine?
A10: Prices can range from a few thousand to several hundred thousand dollars, depending on the type, features, and capacity.
Q11: Is maintenance complicated?
A11: Regular maintenance is essential but usually straightforward, involving routine checks, cleaning, and occasional part replacements.
Q12: Are these machines energy-efficient?
A12: Modern machines are designed to be energy-efficient, though actual efficiency will vary by model and usage.
### Conclusion
Selecting the right meat packaging machine involves understanding your specific requirements and the capabilities of various machines. Always consult with manufacturers and consider future scalability when making a decision.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about meat packaging machine for Buyer Sourcing from China
1. What types of meat packaging machines are available?
There are several types including vacuum packers, tray sealers, thermoformers, and flow wrappers. Each serves different packaging needs such as extending shelf life, minimizing contamination, and maintaining product presentation.
2. What should I consider when sourcing from China?
Look for reliable suppliers with good reviews, check the quality standards they adhere to, ensure they have proper certifications like ISO 9001, and consider the machine’s warranty and after-sales service.
3. How do I verify the quality of the machine?
Request for sample machines or visit the manufacturer’s facility. Also, ask for references from previous buyers and check for international certifications like CE and RoHS.
4. Can the machines handle different types of meat?
Yes, most machines can be adjusted to handle various types of meat including beef, pork, poultry, and seafood. Ensure the machine specifications match your requirements.
5. What is the lead time for delivery?
Lead times can vary. Typically, it ranges from 30 to 60 days after order confirmation and payment. Custom machines may take longer.
6. Are there language barriers in communication?
While many Chinese manufacturers have English-speaking sales teams, it’s beneficial to use clear, simple language and confirm details in writing to avoid misunderstandings.
7. What about after-sales service?
Confirm if the manufacturer offers remote troubleshooting, spare parts supply, and has a local service partner. After-sales support is crucial for machine longevity and performance.
8. How do I handle import duties and taxes?
Consult with a freight forwarder or customs broker to understand the duties, taxes, and import regulations for your country to avoid unexpected costs.
9. Is it possible to get custom machines?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options to suit specific packaging needs. Discuss your requirements in detail and get a prototype before bulk ordering.
10. What payment terms are typically required?
Common payment terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), or Western Union. Ensure you discuss and agree upon payment terms before finalizing the order.