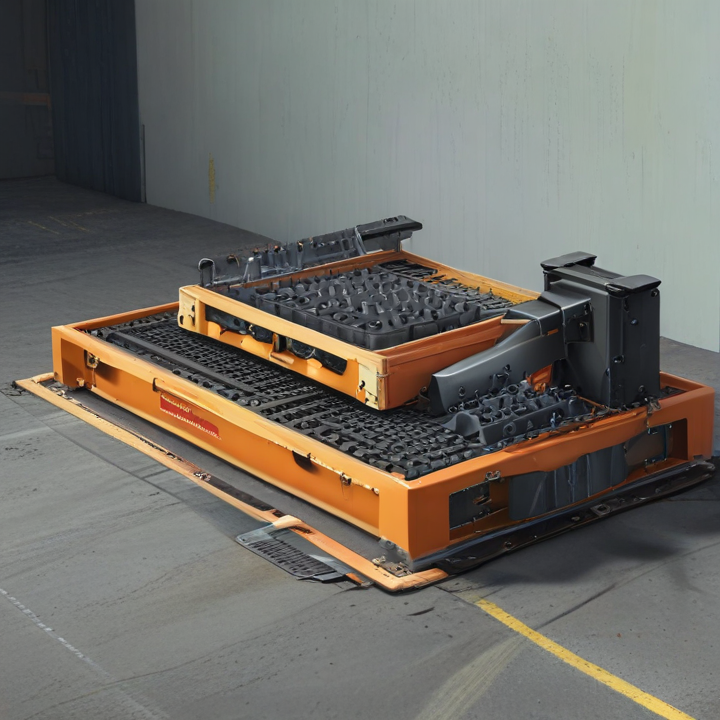
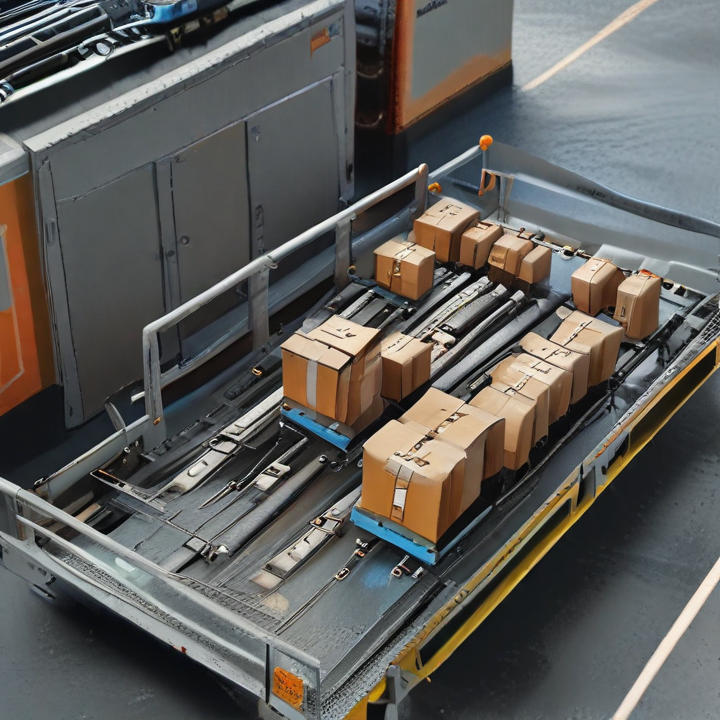
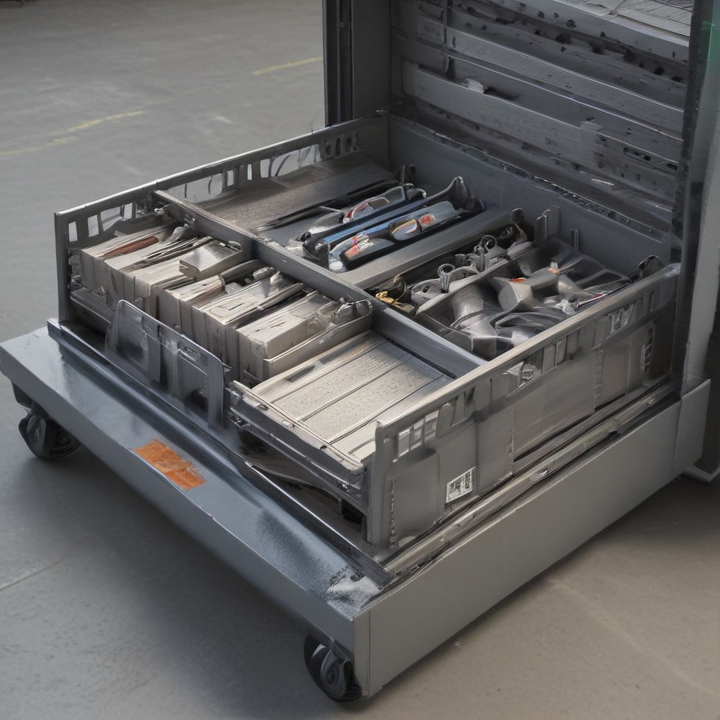
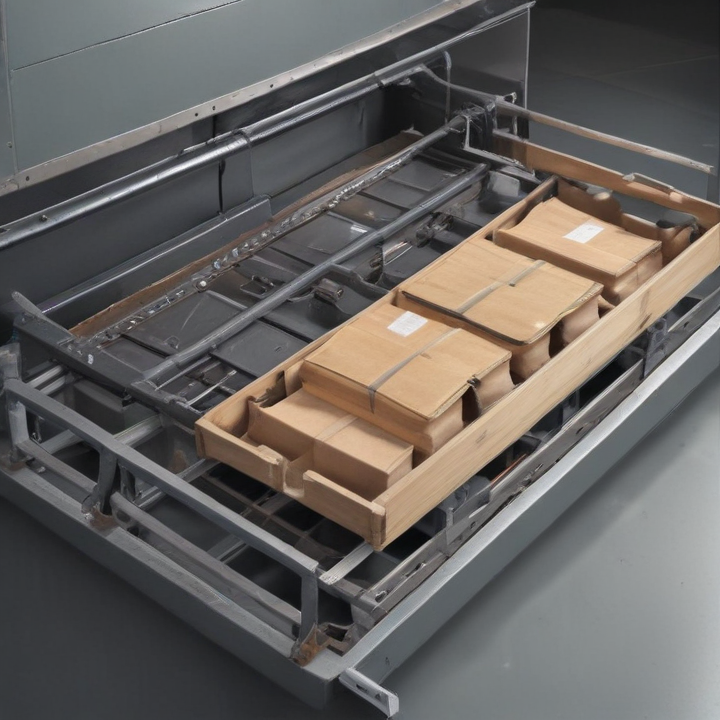
List Technical Parameters of “tray loading equipment”
Certainly, tray loading equipment is crucial in various manufacturing and packaging processes. Here are the technical parameters typically considered for tray loading equipment:
1. Load Capacity: Maximum weight the equipment can handle per tray, typically measured in kilograms or pounds.
2. Tray Dimensions: Specifies the compatible tray sizes, including length, width, and height, usually in millimeters or inches.
3. Loading Speed: Measured in trays per minute (TPM) or parts per minute (PPM), this reflects the operational efficiency.
4. Accuracy: Precision of item placement within trays, often given in millimeters.
5. Power Requirements: Voltage and current specifications, such as 220V AC, 50/60 Hz.
6. Control System: Details on the onboard control units, including PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) type and interface options (e.g., touchscreen HMI, remote control).
7. Drive Mechanism: Types of drives used, such as servo motors, pneumatic systems, or hydraulic actuators.
8. Configuration Options: Flexibility in terms of single or multi-lane configurations to handle different product types simultaneously.
9. Material Handling: Specifications of conveyor belts, robotic arms, or other handling systems incorporated for item transfer and placement.
10. Dimensions and Weight of Equipment: Overall footprint and mass of the equipment, affecting space and mobility considerations.
11. Compatibility: Ability to integrate with other systems like upstream feeding conveyors or downstream packaging machinery.
12. Safety Features: Including emergency stop functions, safety guards, and compliance with safety standards like OSHA or CE certifications.
13. Software: Type of software used for operations, diagnostics, and potential integration with MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems).
14. Operational Environment: Suitable working conditions such as temperature range, humidity, and cleanliness requirements.
15. Maintenance Requirements: Any specific maintenance needs, frequency, and ease of access for repairs.
These parameters ensure the tray loading equipment is chosen or customized to meet the specific needs of a production line or packaging process efficiently and safely.
List Product features of “tray loading equipment”
Certainly! Here are the key product features of “tray loading equipment”:
1. Automated Loading: Tray loading equipment often features automated systems that streamline the process of loading products into trays, reducing manual labor and increasing efficiency.
2. High-Speed Operation: Many models are designed for high-speed operation, capable of handling a large number of trays per minute to meet high production demands.
3. Versatile Tray Compatibility: These machines are usually compatible with various tray sizes and materials, including plastic, aluminum, and cardboard, making them versatile for different applications.
4. Precision and Accuracy: Advanced sensors and control systems ensure precise and accurate placement of products within the trays, minimizing errors and product waste.
5. User-Friendly Interface: Modern tray loading equipment typically features intuitive control panels with touch screens, enabling easy operation, monitoring, and adjustment by operators.
6. Hygienic Design: Especially important in food and pharmaceutical industries, the equipment is often designed with stainless steel construction, easy-to-clean surfaces, and compliance with hygiene standards.
7. Integration Capabilities: These machines can be integrated seamlessly with other systems like upstream conveyors, packaging machines, and robotic arms, creating a fully automated production line.
8. Adjustable Settings: Equipment often includes adjustable settings for different tray loading configurations, enhancing flexibility for various production requirements.
9. Safety Features: Built-in safety mechanisms such as emergency stop buttons, safety guards, and sensors to detect obstructions help protect operators and ensure safe operation.
10. Compact Footprint: Some models are designed with a compact footprint, making them suitable for facilities with limited space while still providing high performance.
11. Durability and Reliability: Tray loading equipment is typically built with robust materials and engineering to ensure long-lasting performance and minimal downtime.
12. Energy Efficiency: Advanced models may include energy-saving modes and components that optimize power usage, contributing to lower operational costs.
These features collectively enhance the efficiency, reliability, and versatility of tray loading equipment, making it a valuable asset in various production environments.
List Application of “tray loading equipment”
Tray loading equipment is widely employed across various industries to automate and streamline the process of loading, unloading, and handling trays or containers. Here are some key applications:
1. Food and Beverage Industry:
– Baking and Confectionery: Automated loading of baking trays with dough or other materials, ensuring uniformity and efficiency.
– Packaged Foods: Loading of food products into trays for packaging and shipping, enhancing speed and reducing manual labor.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry:
– Sterile Processing: Ensuring that pharmaceutical trays are loaded with products in a sterile environment to meet stringent health regulations.
– Research Labs: Organizing samples into trays for systematic analysis and testing.
3. Electronics Manufacturing:
– Component Handling: Loading and unloading of delicate electronic components onto trays for assembly or testing.
– Circuit Board Production: Automated systems place circuit boards onto trays for efficient handling through various production stages.
4. Automotive Industry:
– Parts Assembly: Loading of various automotive parts onto trays for sequential assembly processes.
– Quality Control: Organizing components for systematic inspection and quality testing.
5. Aerospace:
– Precision Component Manufacturing: Handling complex and sensitive aerospace components onto trays for precision assembly and testing.
6. Logistics and Warehousing:
– Order Picking and Packing: Loading items onto trays for faster and more organized order fulfillment.
– Inventory Management: Systematic loading of goods onto trays for better inventory control and tracking.
7. Medical Devices:
– Device Assembly: Loading delicate medical devices onto trays for safe transport and assembly.
– Sterilization: Ensuring that medical devices are properly loaded into trays for autoclaving and sterilization processes.
8. Agriculture:
– Nurseries and Greenhouses: Automating the loading of plant trays for planting, growing, and transporting seedlings.
These applications illustrate the versatility and critical role of tray loading equipment in optimizing production processes, enhancing precision, and reducing labor costs across multiple industries.
List Various Types of “tray loading equipment”
Tray loading equipment is essential for efficiently handling and transporting trays in various industries, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing. Here are several types of tray loading equipment:
1. Manual Tray Loaders:
– Simple devices operated by hand to place products onto trays.
– Suitable for small-scale operations or delicate items.
2. Semi-Automatic Tray Loaders:
– Combine manual and automated processes.
– Typical for medium-scale operations needing some mechanization.
3. Automatic Tray Loaders:
– Fully automated systems that handle products and trays without manual input.
– Ideal for high-volume production lines.
4. Robotic Tray Loaders:
– Use robotic arms for flexible and precise loading.
– Suitable for custom or variable product types and tray configurations.
5. Vertical Tray Loaders:
– Load trays from a vertical position, optimizing floor space.
– Useful in constrained spaces or specific product alignments.
6. Horizontal Tray Loaders:
– Load trays from a horizontal position, offering stability for certain products.
– Common in bakery and confectionary industries.
7. Rotary Tray Loaders:
– Employ a rotating mechanism for loading trays.
– Efficient for applications needing continuous motion.
8. Layered Tray Loaders:
– Designed to load trays in multiple layers.
– Useful in packaging lines that require high stacking efficiency.
9. Conveyor Belt Tray Loaders:
– Integrate with conveyor systems for seamless loading.
– Suitable for continuous production environments.
10. Customized Tray Loaders:
– Tailored to specific industry requirements or unique product specifications.
– Adaptable but often more costly and complex.
Each type of tray loading equipment offers distinct advantages and is chosen based on the specific needs of the production process, product type, and required throughput.
Custom Manufacturing Options for tray loading equipment
When searching for custom manufacturing options for tray loading equipment, several factors come into play to ensure the machinery meets your specific needs. Here are key considerations:
Customization Features:
1. Material Handling Specifications: Tailor the system to accommodate various tray sizes, weights, and materials. This is crucial for industries ranging from food processing to electronics assembly.
2. Automation Level: Decide between semi-automatic and fully automatic systems. Fully automated options often incorporate advanced robotics and sensors for precision and speed, while semi-automatic systems might require some manual intervention.
3. Speed and Throughput: Customize based on the required loading speed and production throughput. High-speed systems are beneficial for large-scale operations, while moderate speed might suffice for smaller production lines.
4. Integration Capabilities: Ensure the equipment can seamlessly integrate with existing production lines. This includes compatibility with conveyance systems, sorting mechanisms, and packaging units.
5. Ergonomics and Safety: Design for operator safety and ergonomics. Features such as adjustable loading heights, safety guards, and emergency stop functions can be included.
6. Software and Controls: Incorporate custom software with user-friendly interfaces to control the equipment. This makes it easier to monitor performance, diagnose issues, and make real-time adjustments.
7. Durability and Maintenance: Choose materials and designs that ensure long-term durability and ease of maintenance. Stainless steel and high-grade aluminum are common choices for their resistance to corrosion and wear.
Consultation and Prototyping:
Working closely with a manufacturer to develop prototype models can help identify any potential issues early on. This iterative process ensures the final product meets your exact requirements.
Cost and ROI:
Lastly, factor in the cost versus the return on investment. Custom tray loading equipment can be a significant investment, but the benefits of increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, and improved safety can justify the expenditure.
Taking these factors into consideration will help in selecting the best custom manufacturing options for your tray loading equipment needs.
List Quality Control and The Manufacturing Process of “tray loading equipment”
Quality Control in Tray Loading Equipment Manufacturing
1. Raw Material Inspection:
– Ensure high-quality materials, like stainless steel and robust polymers, to withstand constant use and handling.
– Conduct thorough visual and chemical examinations to detect any defects or impurities.
2. Precision Manufacturing:
– Utilize CNC machining and laser cutting for accurate dimensions essential for seamless equipment operation.
– Implement stringent tolerance checks to maintain consistency and reliability in assembly.
3. Component Testing:
– Test individual components, such as sensors, actuators, and conveyors, for functionality and durability.
– Use simulated operational conditions to identify potential weaknesses.
4. Assembly Quality Control:
– Adhere to assembly protocols to ensure consistent alignment and secure fitting of parts.
– Employ skilled labor and automated assembly lines for precision and efficiency.
5. Calibration and Alignment:
– Calibrate sensors, actuators, and control systems to ensure precise and reliable performance.
– Conduct alignment checks to guarantee optimal interaction between mechanical and electronic systems.
6. Functional Testing:
– Perform extensive testing of the assembled tray loading equipment to verify correct operation under various load conditions.
– Simulate real-world usage to identify any malfunctions or inefficiencies.
7. Safety Checks:
– Ensure all safety features, like emergency stop buttons and protective guards, are operational and compliant with industry standards.
– Conduct risk assessments to mitigate any hazardous operational conditions.
8. Final Inspection:
– Conduct comprehensive visual and functional inspections before packaging.
– Verify all components are free of defects and the system meets all specified requirements.
Manufacturing Process of Tray Loading Equipment
1. Design and Prototyping:
– Develop detailed CAD models and prototypes to validate design concepts and operational feasibility.
– Iterate designs based on feedback and testing outcomes.
2. Material Sourcing:
– Secure high-quality raw materials and components from trusted suppliers.
– Maintain a rigorous supplier evaluation process to ensure material reliability.
3. Fabrication:
– Use advanced fabrication techniques like CNC machining, welding, and laser cutting to produce precise components.
– Ensure each part meets the design specifications through continuous inspection.
4. Assembly:
– Assemble the tray loading equipment using manual and automated processes.
– Integrate mechanical, electrical, and control systems seamlessly.
5. Quality Assurance Testing:
– Conduct multiple stages of testing, focusing on functionality, safety, and performance integrity.
– Adjust and calibrate as necessary to meet stringent quality standards.

How to use “tray loading equipment”
Tray loading equipment is commonly used in industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing to automate the process of loading products onto trays. Here’s a brief guide on how to use it:
1. Setup:
– Inspect the Equipment: Before use, make sure the tray loading equipment is clean and in good working condition.
– Configure Settings: Adjust the machine settings based on the type and size of products and trays you will be using.
2. Loading Products:
– Place Products on Conveyor: Place the products on the conveyor belt that feeds into the tray loader. Ensure they are properly spaced.
– Check Alignment: Make sure the products are aligned correctly on the conveyor to avoid jams or misplacement.
3. Tray Preparation:
– Load Trays: Insert empty trays into the designated tray-loading area of the machine.
– Adjust Tray Position: Ensure trays are correctly positioned to receive products.
4. Operation:
– Start Machine: Turn on the tray loading equipment using the control panel.
– Monitor Process: Keep an eye on the process to ensure products are being loaded accurately and efficiently onto the trays.
5. Post-Operation:
– Collect Loaded Trays: Once the trays are filled, remove them from the output section of the machine.
– Inspect Loads: Check the trays to ensure products are correctly loaded.
6. Maintenance:
– Clean Equipment: After use, clean the equipment to prevent contamination and ensure longevity.
– Perform Routine Checks: Regularly inspect parts and perform any necessary maintenance.
By following these steps, you can efficiently use tray loading equipment to streamline your production process.
List Properties and Terms of “tray loading equipment”
Tray loading equipment refers to machinery used to load trays automatically or semi-automatically in various industries, such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and manufacturing. Here are some key properties and terms associated with tray loading equipment:
Properties:
1. Automation Level: Can be fully automated or semi-automated depending on the application.
2. Speed: Varies depending on the model, typically measured in trays per minute (TPM).
3. Capacity: The number of trays the equipment can handle at a time or over a fixed period.
4. Versatility: Ability to handle different tray sizes and materials (plastic, metal, etc.).
5. Footprint: The physical space the equipment occupies.
6. Durability: Equipment build quality and material used, ensuring longevity and minimal downtime.
7. Connectivity: Integration with other systems via IoT, sensors, and software for coordinated operation.
8. Ease of Maintenance: Designed for easy access to parts for cleaning, repair, and replacement.
9. Energy Efficiency: Considers power consumption and sustainable operation.
Terms:
1. Conveyor System: Mechanism for moving trays into position for loading.
2. Robotic Arms: Often used for precise placement and loading of items into trays.
3. Sensors: Used for detection and alignment of trays for accurate loading.
4. PLC (Programmable Logic Controller): Brain of the equipment, managing operations and automation processes.
5. Human-Machine Interface (HMI): Touchscreen or control panel for operators to interact with and control the machine.
6. Sorting Mechanism: For organizing items before loading them into trays.
7. Vacuum Suction Grippers: Used for picking and placing items into trays using suction.
8. Pneumatic Systems: Use compressed air for moving mechanical parts.
9. Safety Guarding: Protective features to ensure safe operation and prevent accidents.
10. Stacking/Destacking Mechanism: For arranging loaded or empty trays in stacks.
In conclusion, tray loading equipment streamlines the loading process, increases productivity, and enhances operational efficiency. Its application, level of automation, and integration capabilities determine its suitability for specific industry needs.
List The Evolution history of “tray loading equipment”
The history of tray loading equipment traces back to the early 20th century and has undergone significant technological advancements to meet the evolving demands of various industries, particularly in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Early Developments (Early 1900s – 1950s):
– Manual Systems: Initially, tray loading was a manual process where workers loaded products onto trays for processing or transport.
– Basic Mechanization: Introduction of simple conveyor belts to assist in moving trays, reducing the manual effort but still requiring human intervention for loading.
Automation Begins (1960s – 1980s):
– Semi-Automatic Systems: Integration of basic mechanical systems improved efficiency. Operators guided products onto trays, which were then moved by automated systems.
– Hydraulic and Pneumatic Components: Introduction of hydraulic and pneumatic systems for more precise control and improved handling speeds.
Technological Advancements (1990s – 2000s):
– Robotic Tray Loaders: Emergence of robotic arms capable of picking and placing items onto trays with high precision. Early systems were limited in flexibility and programming complexity.
– PLC and Computer Control: Adoption of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and computer systems enabled better control, customization, and integration with other automated processes.
Modern Era (2010s – Present):
– Advanced Robotics with AI: Modern tray loading equipment now incorporates AI and machine learning, allowing for adaptive, intelligent handling of a wide variety of products. These systems can learn and optimize processes over time.
– High-Speed Automation: Current systems achieve higher speeds and efficiency with lower error rates, crucial for high-demand industries like e-commerce and mass food production.
– Integration with IoT: Internet of Things (IoT) devices provide real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance, significantly reducing downtime.
– Customization and Flexibility: Modern systems offer customization for different product sizes and shapes, vital for industries requiring versatility.
Overall, tray loading equipment has evolved from labor-intensive manual systems to highly sophisticated, automated solutions driven by the latest advancements in robotic and AI technologies.
How to Select a Reliable tray loading equipment
Selecting reliable tray loading equipment involves careful consideration of several factors to ensure it meets your operational needs efficiently. Here are key guidelines to help you make an informed choice:
1. Assess Your Needs: Determine the specific requirements of your operation, including the type of products, loading speed, automation level, and space constraints.
2. Build Quality and Durability: Choose equipment constructed with high-quality materials like stainless steel to withstand rigorous usage and ensure longevity. Check for robust build to handle the specific weight and size of the trays and products.
3. Compatibility: Ensure the equipment is compatible with your existing machinery and processes. It should integrate seamlessly with your production line to avoid disruptions.
4. Technological Features: Look for advanced features such as automation, touch screen controls, programmable settings, and error detection systems that can enhance efficiency and reduce manual intervention.
5. Hygiene and Ease of Cleaning: For industries like food and pharmaceuticals, prioritize equipment designed for easy cleaning and maintenance to meet hygiene standards and prevent contamination.
6. Speed and Efficiency: Evaluate the loading speed and accuracy of the equipment. Ensure it meets or exceeds your production rate requirements without compromising quality.
7. Reputable Manufacturer: Opt for equipment from reputable manufacturers known for reliability and excellent customer support. Research reviews, request references, and consider the manufacturer’s warranty and service packages.
8. Cost-effectiveness: Balance initial cost with long-term value. Consider the total cost of ownership, including maintenance, energy consumption, and potential downtime.
9. Safety Features: Ensure the equipment includes safety mechanisms to protect operators and prevent accidents.
10. Trial and Demonstration: Whenever possible, request a demonstration or trial period to observe the equipment in action and verify it meets your needs.
By systematically evaluating these aspects, you can select reliable tray loading equipment that enhances your production efficiency and longevity.
List “tray loading equipment” FAQ
Tray Loading Equipment FAQ
1. What is tray loading equipment?
Tray loading equipment is machinery designed to automate the placement and management of trays in various industrial processes. It’s commonly used in food processing, pharmaceutical packaging, and electronics manufacturing.
2. What types of tray loading equipment are available?
There are several types, including robotic tray loaders, semi-automatic tray loaders, and fully automatic tray loading systems. The choice depends on the required throughput, product type, and specific industry needs.
3. What are the key benefits of using tray loading equipment?
The primary benefits include increased efficiency, improved precision, reduced labor costs, and enhanced worker safety by minimizing manual handling.
4. What industries commonly use tray loading equipment?
Industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, electronics, and automotive manufacturing typically use these systems to handle and organize their products efficiently.
5. How do I determine the right tray loading system for my needs?
Consider factors like the type of product being handled, production speed, tray size, and layout of your production line. Consult with manufacturers or suppliers for tailored solutions.
6. What are the maintenance requirements for tray loading equipment?
Routine maintenance involves regular cleaning, lubrication of moving parts, inspection for wear and tear, and software updates if applicable. Manufacturer guidelines should be followed.
7. Can tray loading equipment be integrated with existing production lines?
Yes, most tray loading systems are designed to be compatible with existing production lines and can be customized to fit specific requirements.
8. What is the cost of tray loading equipment?
Costs vary widely depending on the type of system, level of automation, and customization. Basic models might start in the low thousands, while advanced systems could reach hundreds of thousands of dollars.
9. Is training required to operate tray loading equipment?
Yes, training is typically required to ensure safe and efficient operation. Manufacturers often provide training during installation.
10. Are there any safety features included?
Modern systems are equipped with safety features such as emergency stop buttons, guarding, and sensors to prevent accidents and ensure operator safety.
This FAQ provides a concise overview of tray loading equipment, addressing common questions to help you understand its applications and benefits.
Top 10 FAQ with answer about tray loading equipment for Buyer Sourcing from China
Certainly! Here are the top 10 frequently asked questions (FAQs) about sourcing tray loading equipment from China:
1. What is the lead time for tray loading equipment from China?
– Typical lead times range from 30 to 60 days, depending on customization requirements and order volume.
2. How can I ensure the quality of the equipment?
– Request samples, visit the manufacturer, and ask for certifications like ISO 9001. Also, use third-party inspection services for quality assurance.
3. What are the payment terms commonly accepted?
– Common terms include T/T (Telegraphic Transfer), L/C (Letter of Credit), and sometimes PayPal for smaller orders. A 30% deposit is often required upfront with the balance paid before shipment.
4. What customization options are available?
– Most manufacturers offer customization for tray dimensions, materials, automation levels, and specific functionalities tailored to your requirements.
5. Is after-sales support available?
– Reputable suppliers usually offer after-sales support, including technical assistance and spare parts. Always confirm this before purchasing.
6. What shipping options do I have?
– Options include sea freight, air freight, and express courier services. Sea freight is the most cost-effective for large orders, while air freight is faster but more expensive.
7. How do I handle import duties and taxes?
– Import duties and taxes vary by country. Consult with a customs broker to understand the costs involved and ensure compliance with local regulations.
8. Are there any specific certifications needed for the equipment to be used in my country?
– Certification requirements vary by country, and may include CE (Europe), UL (USA), and CCC (China). Verify the required certifications in your target market.
9. Can I get references or case studies from the manufacturer?
– Yes, ask the supplier for testimonials or case studies from previous clients to gauge their reliability and performance.
10. What warranty is typically offered on tray loading equipment?
– Warranties usually range from 1 to 2 years. Be sure to understand what the warranty covers and whether it includes parts, labor, or both.
By getting clear answers to these questions, buyers can minimize risks and ensure a smooth sourcing process.




